The cost of conveyor belt depends on multiple variables: material type (rubber, PVC, steel-cord), cover grade (e.g., DIN X, RMA I), width and length, special features (sidewalls, cleats, magnetic modules), and required certifications. Prices range from $8 to $300 per meter, with high-strength or specialized belts incurring significant cost increases. Accurate estimation requires breaking down each component based on usage conditions.
1.Cost of conveyor belt: key input affecting efficiency
“Is there a conveyor belt that costs less than $20 per meter?” Many people always ask this question first when asking for a price. But in fact, such questions often cannot get an accurate answer. The price of a conveyor belt is far from a simple number, but a complex system that is closely tied to working conditions, materials, and design details.
From heavy-duty mining steel cord conveyor belts to light food-grade PU belts, different types of conveyor belts have completely different manufacturing logics and cost models. The cost of a conveyor belt is not static, but a dynamically changing combination variable. It is affected by fluctuations in the raw material market, and is closely related to bandwidth, usage environment, and special functions (such as high temperature resistance, tear resistance, and anti-static).
This guide does not intend to list a bunch of price lists, but hopes to help you answer a core question: how much is a conveyor belt? What is the pricing logic behind it? We will analyze the structure, performance, and additional functions of the conveyor belt layer by layer, as well as how to accurately evaluate the true cost under different configurations, to help you avoid blind purchases and improve decision-making efficiency.

2. Basic knowledge of conveyor belt pricing: Don’t just look at “price per meter”
During the inquiry process, almost every customer will ask: “How much does this conveyor belt cost per meter?” But this question cannot be answered by unit price alone. The calculation method of cost of conveyor belt is far more complicated than imagined. We need to start from three dimensions: structure, working principle and pricing model to truly understand the technical basis behind the quotation.
2.1 Pricing structure is not a unified template, and price per meter is just the “starting point”
The most common quotation unit in the market is “price per meter” or “price per foot”, but the actual price does not have a unified standard, but is dynamically adjusted based on multiple variables. The following is the market reference range in 2025 (the following are all regular size products, and the prices of unconventional size products will be different):
- Ordinary rubber conveyor belt:about $15-$50/m
- PVC/PU food grade conveyor belt:about $8-$30/m
- Heavy-duty steel cord conveyor belt:about $80-$300/m
Special function conveyor belt (high temperature resistant, tear resistant, oil resistant, anti-static, etc.): Since the layers and materials of conveyor belts with different special functions are different, additional fees ranging from 10% to 70% are added to the basic unit price
For example, a 1.2-meter wide rubber belt for coal mines with flame retardant and anti-static functions can be quoted at $110/m. If the basic cost of Steel cord conveyor belt is added, it will be higher; while the same size PVC belt, which is only used to convey packaging cartons, may cost less than $25/m. This also explains why questions such as “how much is a conveyor belt” must be disassembled in combination with use, structure, and function.
2.2 The structure of the conveyor belt determines its cost logic
The first step to understand the pricing of the conveyor belt is to disassemble its physical structure. A standard conveyor belt usually contains the following core layers:
- Cover: determines the wear resistance, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance, and is the key source of the premium. Rubber is more expensive than PVC or PU, and functional coatings (such as food grade, antistatic) further increase the cost.
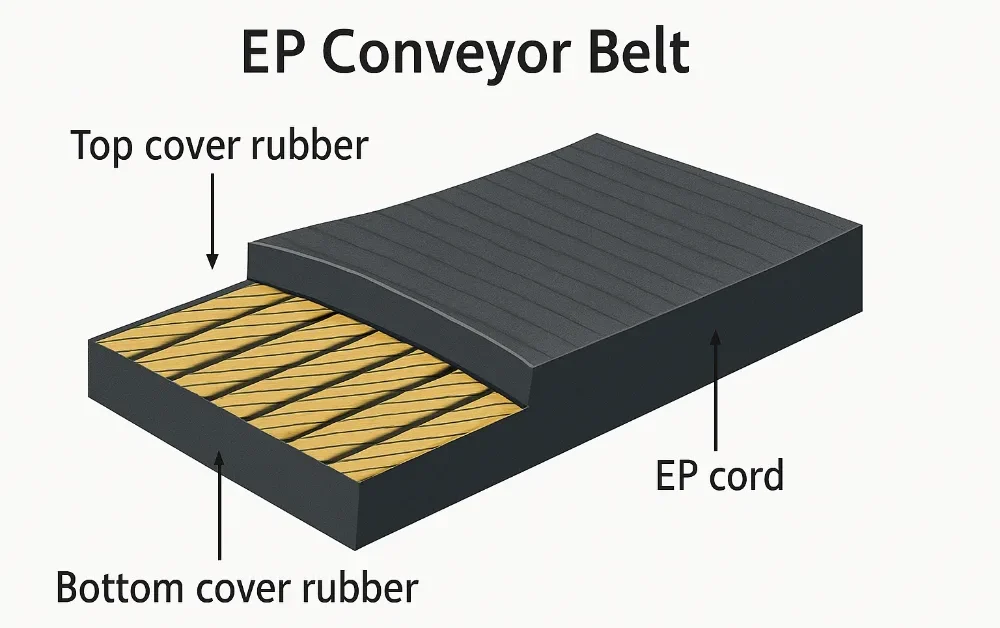
- Carcass: including materials such as polyester, nylon, and steel wire, it is the “skeleton” of the entire conveyor belt. The manufacturing difficulty and material price of wire rope belts are much higher than fabric reinforced belts.
- Reinforcement: used in high-load or high-impact scenarios, such as ore, steel, etc. Structures with transverse rigidity or tear-resistant cloth layers are usually more expensive.
- Sidewalls and baffles (Sidewalls, Cleats):Specially designed structures used to increase the transportation angle or prevent materials from sliding. Each additional type of structure increases the cost by an average of 10% to 30%.
On the other hand, the conveyor belt does not operate independently, it is a part of the entire conveying system. Its working mode directly affects the selection –
- Drive system: Does the belt need to be matched with a variable frequency motor or a constant speed roller?
- Tensioning method:fixed tensioning, screw tensioning or automatic tensioning device? Different methods will affect the tension design and life of the conveyor belt.
- Operation speed and load:Under high-speed operation + heavy load conditions, ordinary materials are difficult to support high wear, and higher-grade materials must be used, which is also one of the key reasons for the price difference.
- Roller spacing: Within the same distance, using a suitable number of rollers can also control costs. In order to maximize the benefits, it is necessary to specifically measure the number of rollers and the corresponding spacing.
Therefore, the cost of conveyor belt is actually a comprehensive evaluation based on “functional adaptability”. It is not a simple length × unit price, but the product of structural complexity × application conditions × performance requirements.
3. Key factors affecting the cost of conveyor belt: from material standards to global dynamics
In actual procurement, “Why do two conveyor belts look similar, but the price is three times different?” This question often troubles purchasing managers and project managers. To accurately understand the cost of conveyor belt, we can’t just focus on the quotation figures, but return to the essential variables such as conveying demand, structural details and supply paths. The following six aspects are the factors we must focus on when evaluating quotations.
3.1 The impact of the cover rubber grade: cost differentiation under international standards
One of the core factors that determine the price of conveyor belts is the performance grade of “cover rubber”. In many quotations, you may see letter codes such as Y, X, W, Z, D, etc. These actually correspond to the cover rubber standard systems of different countries/regions, such as:
- DIN standard (Germany): Y grade is general wear-resistant type, X grade enhances tear strength, W grade enhances wear resistance, and Z grade is basic type. DIN standard is more common in Europe and exports to the Middle East and Africa.
- RMA standard (USA):Grade I (high wear resistance) and Grade II (normal wear resistance) are common grades, widely used in the North American market.
- AS standard (Australia)/ISO standard (international):Some customers will specify ISO 14890 or AS 1332 grade requirements, usually used for international project bidding.
In terms of price, the different grades under these standard systems will directly affect the unit cost:
- RMA Grade II or DIN Z: basic model, about $18–$25/m;
- DIN Y, RMA Grade I:medium wear resistance, about $25–$35/m;
- DIN X/W or ISO T type heat resistant type: high performance grade, the quotation often exceeds $40/m, and some high temperature belts are even close to $55/m.
Note: The price of some basic grade rubber belts (such as DIN Z) under light working conditions may be close to or slightly lower than some PVC conveyor belts, especially in short-distance conveying and low-speed scenarios. This price crossover does not mean performance advantages or disadvantages, but is based on the comprehensive performance of different applications, formulations and processes.
High-grade covering rubber not only improves wear resistance, heat resistance, and tear resistance, but also means higher raw material costs, processing complexity, and quality control requirements. Therefore, it is one of the important dimensions that affect the cost of conveyor belt.

3.2 Material type determines the basic price framework
Material is the most intuitive starting point for pricing and the core of cost differences. Different application scenarios have different requirements for material performance, and the unit price, processing difficulty, and supply stability of each material are also very different.
- Rubber conveyor belt:Common natural rubber, SBR, and NBR materials constitute the basic price range, and the market price in 2025 is $18–$50/m. NBR is suitable for metallurgy and petrochemical industries due to its strong oil resistance, and its price is relatively high among similar products.
- PVC/PU conveyor belt:Suitable for food, tobacco, and logistics industries, with a price range of $8–$30/m. Food-grade PU belts must meet FDA or EU standards, and the unit price is 20% higher on average.
- Fabric reinforced belt (EP/NN): suitable for medium load scenarios, the price is usually $20–$40/m.
- Steel cord conveyor belt: widely used in high tension occasions such as coal mines, cement, ports, etc., the price is as high as $80–$300/m.
- Functional conveyor belt:products with flame retardant, heat resistant, antistatic, acid and alkali resistant properties, require the use of modified rubber or special coatings. The more functions, the more obvious the price superposition, and the highest premium can reach 70%.
This is why “how much is a conveyor belt” cannot be answered with a single number, because the actual quotation is determined by the selected material, working condition adaptation and service life.
3.3 Size parameters determine manufacturing and transportation costs
The length and width of the conveyor belt have a significant impact on the total cost, especially in customized projects.
- Standard width (500mm-1200mm):For every 100mm increase, the cost increases by 8%-10% on average;
- Ultra-wide width (above 2000mm): Customized rolling mills and splicing equipment are required, and the unit cost increases by 2-3 times; (Currently the widest in China can be 5600mm)
At the same time, too long means that the transportation packaging, hoisting, and jointing methods will be upgraded, resulting in additional logistics and construction costs. For example, thinner conveyor belts under 200 meters can usually be shipped in full rolls, but those over 200 meters need to be segmented + spliced on site due to the height limit of the shipping container.

3.4 Structural complexity is the “amplifier” of price differences
Different design features directly determine the manufacturing difficulty and process path. Here are some typical cost drivers:
- Baffle belt:commonly used for material climbing conveying, every 10mm baffle height increase, the cost per meter increases by $3-$5;
- Skirt/sidewall structure:suitable for preventing bulk materials from falling, processing requires high temperature molding or high-strength glue fixation, premium 20-30%;
- Magnetic conveyor belt:requires embedded magnetic blocks and uniform arrangement, manufacturing is complex, and the price per meter increases by $15-$25;
- High temperature resistant structure:such as EPDM, FKM, etc., the unit price of materials is much higher than conventional rubber, and the price of the whole belt increases by more than 1.5 times.
It is recommended to clarify these structural functions in the early stage of design, which can effectively avoid rework or budget overruns in the later stage.
3.5 Regional price differences: transportation and tariffs cannot be ignored
Purchasing location is also an important factor affecting the cost of conveyor belt.
- Made in China:With the advantages of raw materials, labor and production capacity clusters, the price of the same specifications is generally 30%-50% lower than that in Europe and the United States, which is suitable for large-scale and customized projects;
- Made in Europe, the United States, Japan and South Korea:It has special certification, brand premium or high value-added structure, but the transportation, tariff and MOQ requirements are higher.
Taking the data in 2025 as an example, a 1200mm wide, DIN Y grade rubber belt is quoted at about $160/meter in Europe and the United States, while the domestic customized quotation may be between $85-$95/meter, and the price difference is almost doubled.
3.6 Market dynamics are the “behind-the-scenes pusher” of price fluctuations
Raw material fluctuations are the decisive external variables. Data from Q1 2025 show:
- Natural rubber prices rose by 12% year-on-year
- Steel raw material prices rose by 9%
- Sea transportation costs remain high
Such fluctuations will be quickly transmitted to terminal quotations. Therefore, it is recommended to lock prices as early as possible in large projects, or deliver in stages to hedge market risks.
From the level of cover glue to the complexity of the structure, from the material system to the global procurement path, the cost of conveyor belt is actually a combination of a set of dynamic factors, rather than a simple “price per meter” calculation. Only by striking a balance between technology, application and budget can a truly reasonable procurement decision be made.
4.The truth about the non-standard cost of conveyor belt
The cost of standard conveyor belts still has rules to follow, but once it enters the application scenario of high strength, special working conditions or customized functions, the cost of conveyor belt will present a more complex multi-factor superposition state. In this section, we will use typical industry cases to specifically disassemble the cost structure of special conveyor belts and analyze the procurement logic behind them.
4.1 Heavy material transportation scenario: the main reason for the increase in cost is not “thick skin”
In heavy-duty industries such as mines, ports, and sand and gravel plants, conveyor belts need to withstand challenges such as continuous impact, coarse grain wear, and high-frequency operation. Steel Cord Conveyor Belt or high-strength fabric-reinforced rubber belts are often used in such scenarios.
Take a 1600mm wide, 5+5 cover rubber, DIN X grade steel cable conveyor belt used in South African gold mines as an example. The delivery price in 2025 is:
- Unit cost: $180/m
- Total length: 320 meters
- Total price:about $57,600, excluding installation and joint costs
Among them, the cover rubber formula (wear-resistant + tear-resistant) accounts for 42% of the total cost, the steel cable tension structure cost accounts for 28%, the manufacturing process and special mold costs account for 15%, and the rest is packaging, transportation and joint processing.
Since such conveyor belts usually need to be matched with high-load rollers, emergency brakes and multi-point tensioning systems, it is recommended to package the budget as a whole in the early stage of the project, rather than asking for a separate price of “how much per meter”.

4.2 Wide conveyor belt: complex structure + equipment upgrade = cost jump
Many large-scale bulk material conveying systems will choose large-size conveyor belts with a width of more than 2000mm to increase single throughput. However, many purchasers do not realize that the increase in width not only means an increase in materials, but also involves equipment upgrades, changes in splicing methods and a decrease in manufacturing cycle.
The following is a quotation example for a 3000mm wide, 4-layer EP structure custom rubber belt:
- Basic material cost: $45/m (based on the same formula 1200mm belt)
- Additional cost of ultra-wide processing: +$28/m (including wide-width calendering, splicing process, and material loss)
- Final unit price: $73/m
- Minimum order quantity:200 meters
During the design stage, the customer originally planned to use one wide belt, but after simulation, we recommended running two 1500mm belts in parallel, saving nearly 30% of the belt cost, while simplifying the installation process and tension control strategy.
In this scenario, the cost of conveyor belt is no longer a single calculation logic, but is bound to system variables such as process design, factory capacity, and construction matching. It is recommended to evaluate multiple structural configurations in advance during the technical review stage.
4.3 Special Functional Belts: Each “Performance Option” is Equal to a Budget
Functional conveyor belts seem to be just “adding a little function”, but in fact, behind them are formula modification, coating changes, and process reconstruction. For example:
Conveyor Belt Type | Functionality Additions  | Unit Price Premium Range ($/meter)  | Typical Application Industries |
Flame retardant rubber conveyor belts  | Conforms to DIN K or ISO 340 | +$10~$18 | Coal mines, tunnels, timber mills |
Food grade PU belts | Conforms to FDA/EU standards  | +$8~$15 | Food processing, packaging |
Antistatic Rubber Conveyor Belt  | Surface resistance <3×10⁸Ω  | +$5~$10 | Fertilizer, powder, electronic materials |
High temperature resistant belt (>200°C) | EPDM rubber, silicone layer | +$20~$35 | Cement, steel plant, kiln area |
For example, a high-temperature belt used by a steel plant has a unit price of $92/m, which is 70% higher than ordinary rubber belts. However, the average service life is extended from 9 months to 26 months, and the annual replacement frequency is reduced by 70%, and the actual unit cost is better.
Behind this “reasonably expensive” design is the value matching customized according to the working conditions. If you only pursue low prices and ignore feature adaptation, it will often lead to frequent subsequent replacements and production interruptions, which will increase the total investment in the long term.
In the process of selecting a special conveyor belt, the unit price is only one of the reference values. What really needs to be confirmed is whether this belt can withstand your material characteristics, equipment structure and actual operating rhythm.
Only by putting the “cost of conveyor belt” back into the overall use cycle, failure risk and maintenance difficulty can a more reasonable budget judgment be made. Otherwise, the seemingly cheap choice may be the starting point of long-term costs.

5.Hidden Costs in the Cost of Conveyor Belt
Even if we have mastered the cost variables such as materials, size, and structure, the “external costs” that are not directly written on the quotation are often the ones that really affect the total expenditure. The cost of conveyor belt is not just the purchase budget, it also includes a whole set of extended expenses such as installation efficiency, operating energy consumption, transportation costs, maintenance cycles, and equipment adaptability. In this section, we will systematically analyze these hidden costs to help you establish a more complete evaluation logic.
5.1 Installation and maintenance costs: underestimated long-term expenditures
Many buyers ignore the difference in installation costs when comparing quotations, especially when customizing structures, extra-long belts, and special-shaped designs. This part of the cost may be as high as 20%-40% of the product cost.
Taking the steel cord conveyor belt as an example, its joints are usually hot-vulcanized, and the tools, personnel, and time costs required are much higher than ordinary fabric belts. In a port project in Southeast Asia in 2025, a 280-meter-long heavy-duty belt has a joint and installation cost of $9,800, equivalent to 26% of the purchase cost of the entire belt.
In addition, maintenance strategies also directly affect long-term costs:
- Passive maintenance (repair by fault): saves money in the short term, but is costly in the long term, often accompanied by sudden downtime;
- Preventive maintenance (regular overhaul): moderate strategy, suitable for most continuous operating environments;
- Predictive maintenance (data monitoring):high initial investment, but can significantly reduce the risk of unexpected downtime for high-value industries (such as mines and power plants).
Therefore, when calculating how much is a conveyor belt, it is better to extend the “price of the first meter” backward to see the maintenance rhythm and labor input throughout the entire operating cycle.
5.2 Energy efficiency and environmental considerations: variables that are changing the cost structure
As a continuous power device, the energy consumption cost of the conveyor system cannot be ignored. The elastic modulus, surface friction coefficient and deadweight of the belt itself will affect the power consumption of the whole machine.
Some companies use low rolling resistance structure and lightweight skeleton materials. Although the unit price of the belt increases by about 8%-15%, the energy consumption can be reduced by 6%-12% in long-term operation. For systems with an annual operating time of more than 5,000 hours, the power saving effect is very obvious.
Environmental protection policies are also forcing the transformation of material structure, such as:
- Recycled rubber formula:reduce material costs;
- Recyclable skeleton: conducive to recycling and decomposition;
- Low smoke halogen-free flame retardant:in line with international environmental regulations, price premium of more than 20%.
Incorporating these variables into the decision-making of cost of conveyor belt is not only related to compliance, but also to the brand and operation and maintenance efficiency of the enterprise.
5.3 Freight: length, thickness, and cabinet type selection are the core cost variables
In international procurement scenarios, transportation costs are often underestimated. In fact, it is an important part of the cost of conveyor belt, especially in medium and long-distance shipping projects.
First of all, it should be made clear that whether to ship in full containers does not depend on the width itself, but on the total length, thickness and roll diameter of the conveyor belt. For example, a 1600mm wide conveyor belt can still be fully loaded into a 40HQ container if the thickness is properly controlled; but if the roll diameter is too large or the length exceeds the standard, even if the width is narrow, it may need to be split or switched to an open top container.
From our actual experience, when the value of the goods is close to $20,000, the conditions for full container shipment are usually met, and the freight structure is relatively stable. However, it should be emphasized that this judgment is based on experience, not a unified industry standard, and it also needs to be combined with order density, loading method and transportation area.
Take a batch of conveyor belts we recently sent to Mali customers as an example. The batch of goods was shipped to the port of Senegal via a 40HQ container. The full container value was $70,000 and the transportation cost was $6,400. The unit freight cost is reasonable, the loading efficiency is high, and the overall transportation cost ratio is controllable.
On the contrary, if the order volume is small, for example, less than 100 meters, or the thickness and roll diameter make it impossible to load the container efficiently, not only may there be the cost of consolidation and reinforcement, but also repeated loading and unloading or non-standard port miscellaneous goods, and the unit transportation cost will quickly rise by 30%-50%.
Therefore, when evaluating the cost of conveyor belt, it is recommended to directly include the freight in the product structure, rather than waiting until the customs declaration stage to add it separately, which is particularly critical for budget control and decision-making.

5.4 Total Lifecycle Cost (TLC): The real indicator for engineering decision-making
In large projects, decision makers are increasingly concerned about the “total lifecycle cost” (Total Lifecycle Cost, TLC), that is, not only the purchase price, but also the sum of the subsequent operation, maintenance, transportation and other stages of expenditure.
The following is a TLC comparison model (based on 100 meters of belt body), which has taken into account the installation, maintenance and transportation costs:
Project Stage  | Standard Rubber Belt ($/meter) | High-performance wear-resistant belt ($/m) |
Initial Purchase Cost  | $28  | $45 |
Installation + Fitting Costs | $6 | $7 |
Shipping cost | $5 | $5 |
Average annual maintenance cost | $9 | $4 |
Average Replacement Cycle (years) | 1.5 years | 3 years |
Total Annualized Cost  | $37.6  | $27.6 |
It can be seen that although the initial investment of high-performance conveyor belts is higher, their annualized use cost is significantly lower due to their longer life and lower maintenance costs. For industries with high requirements for production line stability, such as ports, mines, and power plants, this logic of “spending a little more in advance and saving a lot later” has become the mainstream selection standard.
6.How to accurately estimate the cost of conveyor belt
Many companies habitually draw a formula at the beginning of the selection: “length × price per meter = budget”. It sounds concise and clear, but problems often arise during implementation. Unclear material selection, missing functional parameters, ignoring transportation methods… Once these cost variables are exposed in the later stage, the loss is not only the budget, but also the project progress and organizational reputation.
When we contact various customers and projects, we find a trend: those companies that have the ability to estimate the cost of conveyor belt are often more proactive in controlling the rhythm and cost. And those teams that only promote projects by “comparing prices” often end up in a situation of “either delay or rework”.
6.1 Why should we pay attention to conveyor belt cost estimation?
In project management, price is only one of the input variables, and more importantly, how it affects the execution chain. If the cost estimate is inaccurate, common consequences include:
- The quotation is seriously deviated from the actual order, affecting the payment and delivery rhythm;
- Rework is caused by unclear parameters during the installation phase;
- The cost model does not include transportation or installation, resulting in total expenditure out of control;
The accurate disassembly of the cost of conveyor belt can help the project team take the initiative, from material selection to cabinet installation, from delivery date to life cycle, the cost is no longer “post-settlement”, but “early control”.
6.2 Standard process for conveyor belt cost estimation
The following is a set of feasible and reusable estimation processes, which are suitable for the initial stage of the project or the scheme evaluation stage:
Step 1: Clarify technical parameters
- Material requirements: rubber (SBR, NBR), PVC, steel cable core, EP cloth layer
- Structural specifications:width, thickness, number of layers, whether there is a baffle/skirt/magnetic module
- Working environment:temperature, humidity, material properties (abrasion/adhesion/particle size)
- Certification requirements:whether it involves food grade, antistatic, flame retardant standards
Step 2: Get a belt quote
- Ask the supplier to disassemble the quotation structure: material + processing + additional functions + packaging + EXW or FOB price
- Pay special attention to whether it contains joints, whether it contains test reports, whether it is spot or customized
Step 3: Calculate additional costs
- Installation costs: joint form (mechanical/cold bonding/hot vulcanization), installation method (on-site vs factory pre-connection), whether lifting is required
- Freight estimate:full cabinet vs LCL, second-stage transportation at the destination port, loading and unloading requirements, etc.
Step 4: Establish a total project cost model.
Combine the belt cost, transportation, installation, estimated maintenance, etc. to establish a “total cost per meter” or “total project budget” model as the basis for internal decision-making.
At this time, you will find that “how much is a conveyor belt” is no longer a question that can be answered verbally.
6.3 Several key points to improve the accuracy of estimates
- Split variables in advance:let suppliers break down the quotation according to “belt + additional functions + installation + freight”
- Establish internal price comparison records: precipitate the real cost of historical projects as the basis for the next round of negotiations
- Switch the evaluation unit: do not use “unit price” anymore, it is recommended to directly change to “delivery cost of the entire line”
- Focus on two hidden costs:transportation method and joint process – these two are most likely to exceed the budget
The price per meter is indeed the entry point for purchasing, but it is definitely not the exit for decision-making. What really affects the delivery rhythm and operation and maintenance stability is whether you have incorporated these invisible expenditure factors into the model in advance. The cost of conveyor belt is ultimately a reflection of your deep understanding of the project, rather than a superficial game of a string of numbers.

7. Key points for judging the purchase of conveyor belts
If the estimated cost is to let you understand where the budget comes from, then the “selection” stage before placing an order is the key to determine the success or failure of the project. When we were docking with multiple actual projects, we found that the systems that really run stable conveyor belts were not won by the lowest quotation, but were based on clear cognition, correct judgment and system procurement strategy.
The following are several judgment skills that are worth serious consideration before purchasing:
1. Don’t just listen to the quotation, but judge whether the other party can accurately understand the drawings and parameters
The parameters of most conveyor belt projects are given by the users themselves, but the factory really knows how to convert them into structural processes. You can try to send your own demand drawings/specifications to the other party to see if he returns a structural plan and quotation breakdown, rather than “reporting a number off the top of your head”.
2. Don’t pursue “the more functions the better”, but judge “which functions are necessary”
Flame retardant, heat resistant, anti-static, skirt, baffle… Every time a function is added, the price will increase by one level. It is recommended to return to the material properties and equipment design to confirm whether it is really needed. If your material is not sticky, slippery, or hot, then installing an anti-slip baffle is a pure waste.
3. Don’t ignore delivery stability and after-sales capabilities
Price can be negotiated, but no one can compensate you for lost work if delivery is delayed. Give priority to suppliers with stable production rhythm, clear technical handover process, and response mechanism, rather than factories that only quote fast prices.
4. The key is to see whether the other party has worked in your country or surrounding markets, rather than simply asking if he has worked in this industry
Conveyor belts are typical customized products, and most suppliers can do it. But if he has shipped to your country or port, he can usually immediately respond to how long the shipping time is, whether 40HQ is often used in the local area, and whether specific certification/packaging requirements are required. This “subconscious reaction” to the rhythm of the regional market is the basis for judging whether it can cooperate quickly. The larger the supplier, the more markets it covers, and the lower your communication and delivery risks.
8.Conveyor belt maintenance and troubleshooting guide
Even if the selection is appropriate, if the subsequent maintenance is not in place, the conveyor belt will still be scrapped in advance, and even cause the entire line to stop working. We have summarized several key maintenance points that are most easily overlooked in daily use, as well as the judgment logic of typical faults, for reference by users.
1. Daily maintenance focus: three inspections and three checks
- Check the tension: Insufficient tension will cause slippage, and excessive tension will accelerate bearing wear. The state of the tensioning device should be checked regularly to avoid long-term deviation from the set value.
- Check the deviation:Deviation is one of the common problems of the conveyor belt system, which is mainly related to the position of the roller, the accuracy of the roller, and the drop of the material. The roller and the deviation adjustment device should be calibrated regularly.
- Check the wear: Especially the skirt and baffle parts, if there is abnormal glue loss, local scratches, and cracks, the machine should be stopped in time to prevent the crack from expanding.
At the same time, it is recommended to conduct the following special inspections at least once a month:
- Check the joint area:whether the hot vulcanization or mechanical buckle is loose, cracked, or aging;
- Check the sweeper and the material drop point:whether there is rubber accumulation and whether it affects the surface integrity of the belt;
- Check the drive device and motor load:whether there is abnormal current fluctuation to prevent the belt from “not being dragged”.
2. Quick judgment logic for common problems
- Belt shaking: mostly uneven rollers, uneven belt thickness, or unbuffered material impact;
- Belt slippage:It may be insufficient tension or roller surface slippage (it is recommended to add a rubber layer or increase preload);
- Belt tearing or edge curling:Check whether the material is stuck at the guide trough, or whether the belt is running with long-term partial load;
- Belt abnormal noise or strong pulling feeling:It is necessary to check the concentricity of the roller, the bearing clearance and the coaxial accuracy of the roller;

9. Market Trends and Future Insights (2025 and Beyond)
Contrary to what many people understand, the conveyor belt industry is not “too traditional”. Instead, it is experiencing a round of industrial re-growth driven by the global infrastructure cycle and manufacturing transfer. If you are observing the purchasing trends or market opportunities in this industry, the following trends cannot be ignored.
1. Post-war reconstruction and energy transformation will become the driving force for new demand
Since 2024, Ukraine’s post-war reconstruction plan has been launched one after another, and many cement plants, steel plants, and port projects have been restarted, and the demand for heavy-duty rubber conveyor belts, high-temperature belts, and wear-resistant belts has increased significantly.
At the same time, infrastructure and resource-based exporting countries in the Middle East and Africa, such as Angola and Nigeria, have also increased their investment in the construction of mines, roads and ports in their own countries after improving oil and gas revenues.
In these markets, standardized products are difficult to meet the complex needs of the on-site environment, and customers are more inclined to look for suppliers who can customize structures and respond quickly. For conveyor-belt-manufacturers, this is a window period from “price competition” to “engineering matching ability competition”.
2. Orders from South America and Southeast Asia are steadily increasing
Take South America as an example. The mineral processing industries in Chile, Peru, Brazil and other countries have a stable demand for steel cord belts and special tear-resistant belts; while Vietnam, Indonesia, Thailand and other countries are rapidly introducing PVC and PU light conveyor belt systems due to the transfer of logistics, food, and warehousing manufacturing.
Purchasers in these regions pay more attention to delivery control capabilities, language communication efficiency and after-sales mechanisms, rather than simply competing for the lowest cost. The past “product-to-product” procurement logic is being upgraded to a “service-to-delivery capability” selection method.

3. Technology trends: digital monitoring and environmentally friendly materials will become differentiated standard features
It is expected that starting in 2025, more companies around the world will try to integrate Internet of Things monitoring systems (IoT) into conveyor lines, including tension sensors, temperature anomalies, deviation alarms, etc.; at the same time, conveyor belts exported to the European and American markets will also face stricter environmental compliance, such as REACH, RoHS, and low-smoke halogen-free standards.
This trend forces factories to plan ahead for a “monitorable, recyclable, and certifiable” product system, otherwise they will gradually lose their entry into the high value-added market.
10. FAQ
Q1: Cost of conveyor belt How much is it per meter?
Prices vary greatly under different materials and working conditions. The common price of rubber conveyor belt is $15-50/meter, PVC belt is about $8-30/meter, and steel cord belt can reach $80-300/meter. Special functions (such as flame retardant, tear-resistant) or ultra-wide customization will significantly increase the unit price.
Q2: How do I know which conveyor belt is suitable for my industry?
First confirm the material properties (temperature, abrasion, corrosion), and then combine the conveying length, running speed and equipment structure selection. If you are not sure, you can provide usage scenarios, photos or technical parameters to let the factory recommend the structure. Don’t just talk about the purpose, talk about the parameters. For example, when you need a heat-resistant belt, you need to know what range the temperature of your usage scenario is generally in.
Q3: How to calculate the cost per foot of conveyor belt?
1 meter ≈ 3.28 feet, so just divide the price per meter by 3.28 to get the cost per foot. For example, $32/meter ≈ $9.76/foot. Note: Additional functions, joint methods, packaging and transportation, etc. must also be considered to be the real cost.
Q4: Is there a minimum order quantity? Can small orders be shipped?
Most projects recommend a minimum order quantity of about 200 meters, which is convenient for rolling, loading, and diluting transportation and packaging costs. Although small customization is supported, if it is lower than this length, the cost per meter and freight will increase significantly. It is recommended to combine other materials for shipment. It is more cost-effective.
Q5: How to avoid serious deviations in the conveyor belt budget?
It is recommended to ask suppliers to split the quotation structure from the beginning, including belt body price, special functions, joint form and transportation method. Don’t just look at “how much per meter”, but take into account the delivery cost of the entire roll and the maintenance frequency during the life cycle.
All the data we share are derived from industry experience and public market analysis to help you form cost judgment logic. If you happen to have project requirements, please contact us for detailed structure and quotation information.