1. The Importance of Conveyor Belt Alignment
Conveyor belt alignment is an important but often overlooked problem that many companies only think about when there are serious problems with the conveyor belt. This problem is like not having a “four-wheel alignment” on the wheels. At first, the car will only have slight steering wheel shake and other problems, but as time goes by, small problems will gradually magnify. Improper conveyor belt alignment will cause a series of problems that not only affect production efficiency, but may also cause long-term damage to the conveyor equipment.
If the conveyor belt is not aligned, the belt will gradually deviate to one side, which will cause uneven force on both sides, followed by a tilt of the conveyor belt surface. This deviation will affect other components of the conveyor system over time, such as drive wheels, rollers, etc., causing them additional damage and abnormal wear.
Another problem with conveyor belt deviation is reduced energy efficiency. When the contact between the belt and the roller or other components is asymmetrical, the friction will increase, causing the system to require more energy to maintain the normal operation of the conveyor belt. The result is increased power consumption and higher operating costs for the company.
And when the conveyor belt is offset, the material conveying will be disturbed, and the conveyor belt surface will have abnormal shaking, causing the material to shake out from both sides. This will seriously affect the quality of product production and material waste. How to square conveyor belts becomes a crucial step. This is the importance of Conveyor Belt Alignment
Correct conveyor belt alignment can stabilize the operating efficiency of the equipment and its service life, and can also reduce unnecessary downtime and maintenance. In order to keep the production line smooth, ensure that each component is in the right position, this is the real value of conveyor belt alignment.
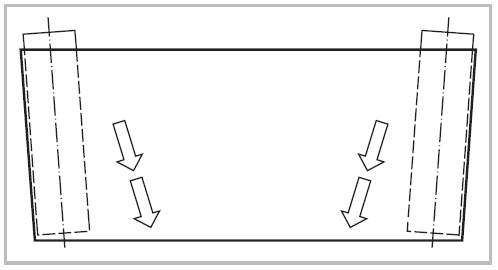
2. Conveyor Belt Alignment Basics
2.1 How to Square Conveyor Belts
Before you begin to align your conveyor belts, you must first understand how to square conveyor belts. This requires a careful inspection of the various components of the conveyor belt to ensure that each part is in the correct position.
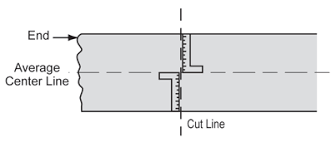
When aligning, first determine the centerline of the conveyor belt. This centerline will become the reference line during the alignment process. Measure and mark the center point of the conveyor belt from both sides of the conveyor belt. The line parallel to the sides of the conveyor belt and passing through the center point is the centerline.
If during the operation and commissioning process, the belt begins to shift to one side by observing the direction of movement of the centerline to confirm whether there is any deviation, it must be adjusted in time to prevent increased wear or damage to other parts.
2.2 The Role of Conveyor Components in Alignment
Conveyor belt alignment is not only about adjusting the belt itself, it also involves many other important conveyor system components. Including pulleys, rollers, idlers, etc., all must be kept in the correct position. These components work together to ensure the proper operation of the conveyor belt.
The alignment of the head pulleys and tail pulleys must be very precise. If the pulleys of these two parts are misaligned, the conveyor belt’s path will be affected and the belt will deviate.
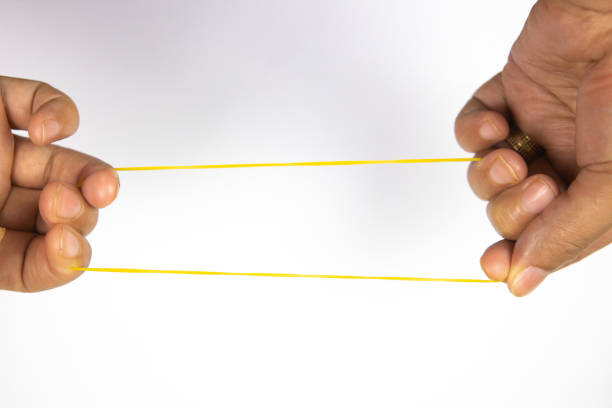
It is like pulling a rectangle with a rubber band. Once one side is displaced, it will become a parallelogram. At this time, the two long sides of the rubber band will be offset. Misalignment of the pulleys, tensioners and guide wheels will also increase friction and uneven force, further affecting the stability of the conveyor belt.
2.3 The Importance of Belt Material in Alignment
Different conveyor belt materials may have different effects on the alignment requirements. Belt material is another key factor affecting conveyor belt alignment. For example, rubber conveyor belts are tougher than PVC conveyor belts and require more attention to ensure that they can maintain alignment under heavy loads. If the conveyor belt is too loose or unevenly tensioned, it will easily slip or deviate, so the alignment of rubber conveyor belts is more difficult.
PVC conveyor belts are relatively easy to align. But this does not mean that PVC conveyor belts do not need regular inspections, especially under working conditions that are greatly affected by ambient temperature changes. Changes in humidity or temperature may cause small changes in the size of PVC conveyor belts, thereby affecting the alignment accuracy. Therefore, whether it is a rubber conveyor belt or a PVC conveyor belt, regular inspection and adjustment are crucial.

2.4 Benefits of Proper Conveyor Belt Alignment
Mastering the basic skills of conveyor belt alignment can not only effectively prevent the belt from deviating from the track, but also bring many other benefits.
- ① Proper alignment can greatly reduce the wear of the conveyor belt and extend its service life. The “Conveyor Maintenance Manual” mentions that improper alignment will increase the wear rate of the conveyor belt by about 15%-25%, which means that the service life of the conveyor belt is greatly shortened.
- ② Maintaining good alignment can ensure the efficient operation of the equipment and reduce unnecessary downtime. Frequent equipment failures and downtime will inevitably lead to a decrease in production efficiency.
According to the data in the book “Conveyor Belt System Troubleshooting and Maintenance”, conveyor belt deviation and equipment failure are one of the main reasons for production line downtime, accounting for 15%-20% of downtime.
- ③ Correct alignment also helps improve energy efficiency, thereby reducing energy consumption and saving operating costs. When the conveyor belt is not properly aligned, friction increases and energy consumption increases.
The research report “Energy Efficiency in Conveyor Systems” mentioned that if there is a problem with the alignment of the conveyor belt, there will usually be 10%-20% more excess loss of electricity, which is a cost that cannot be ignored for large-scale production.

2.5 Regular Monitoring and Adjustments
In order to ensure that the conveyor belt always stays on the right track, it is equally important to know how to track conveyor belt. Regularly monitoring the alignment of the conveyor belt and making necessary adjustments is the key to keeping the production line running smoothly. Through visual inspection, marking method, laser alignment tool, and using a tension meter to check tension uniformity.
Through regular inspection and adjustment, it can ensure that the conveyor belt is always in the best condition during the production process, thereby minimizing potential failures and damage. Preventing an incident is always cheaper than making up for it after the incident.

3. Tools Needed for Conveyor Belt Alignment
As mentioned earlier, accurate conveyor belt alignment is essential, and one of the keys to achieving this goal is to choose the right tools. Using professional tools can ensure that each adjustment is more accurate, reduce rework caused by operating errors, thereby improving overall work efficiency and ensuring that the conveyor belt always maintains optimal operation.
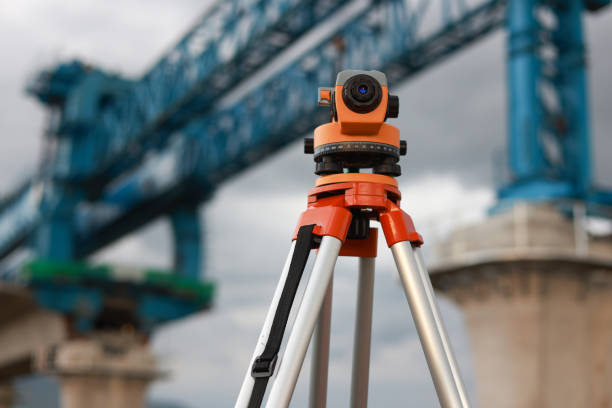
3.1 Theodolite for Accurate Measurements
Theodolite is used to accurately measure the angle and direction of the conveyor belt. When operating, first fix the theodolite to one end of the conveyor belt to ensure that it is level. Then, adjust the angle of the instrument to align the head and tail rollers of the conveyor belt and measure the alignment between the two. With this method, you can clearly know the degree of deviation of the conveyor belt and make adjustments based on the measurement results to ensure alignment.Suitable for use in large-scale projects.

3.2 Surveyor’s level for Maintaining Even Surfaces
The carpenter’s level is used to check whether the conveyor belt system is level. When using, place the level on the support frame of the conveyor belt to ensure that it is in contact with the surface of the conveyor belt. If the bubble of the level is off-center, it means that the conveyor belt is tilted. You need to adjust the conveyor belt support until the bubble is centered to ensure that the conveyor belt is level and reduce friction and wear caused by tilting.
Tip: This method is only suitable for short-distance conveyor belts. For conveyor belts that are too long or too wide, a level ruler cannot be used to operate because the conveyor belt will naturally sag in the middle.

3.3 Chalk Line for Reference Markings
The chalk line is used to mark reference lines (especially the center line) on the conveyor belt surface or support. When operating, first fix the starting point of the chalk line at one end of the conveyor belt, then straighten the chalk line and let it touch the other end to ensure that it is pulled tight. Next, use the chalk line to mark a clear alignment line on the conveyor belt surface as a standard line for reference during the adjustment process. This line can help you ensure that the conveyor belt runs along the correct track during adjustment.

3.4 Tape Measure for Precision Alignment
The tape measure is used to measure distances and gaps during the alignment process of the conveyor belt. You can use a tape measure to measure the distance between the center line of the conveyor belt and the two side brackets, and measure the distance between the two side edges of the conveyor belt and the two side brackets to ensure that the data measured from the same point is the same. This can help you ensure that the tension on both sides of the conveyor belt is consistent, thereby avoiding problems caused by uneven tension.
3.5 Plumb Bob for Vertical Reference Lines
The plumb bob is used to ensure the vertical alignment of the head and tail rollers of the conveyor belt. When operating, fix the hook of the plumb bob to the top of the conveyor belt roller and let the weight hang naturally to ensure that the line is vertical. Check whether the vertical line and the conveyor belt frame are aligned. If the vertical line deviates from the frame, you need to adjust the conveyor belt rollers until they are vertically aligned.

3.6 Caliper for Checking Rollers and Frames
The Caliper is used to check the alignment of the conveyor belt frame and rollers. When operating, place the Caliper along the conveyor belt rollers and brackets to observe whether there are any deviations. If there is a gap between the Caliper and the frame or roller, it means that they are not aligned. You need to adjust the rollers or brackets according to the measurement results until they are parallel to the Caliper to ensure that the equipment is in the correct position.
3.7 Inspecting the Conveyor Frame for Alignment Issues
Inspecting the conveyor frame for alignment issues is key to ensuring the normal operation of the system. When operating, first observe whether there is obvious deformation or damage to the support points of the frame. If the frame is found to be deformed, tools can be used to correct it to ensure that the frame remains straight and level. In addition, a carpenter’s level can be used to check the level of the frame to ensure that there is no tilt. If the frame is not aligned properly, it will directly affect the operation of the conveyor belt.
4. 7 Steps to Complete Conveyor Belt Alignment
Although the steps are simple, there may be some challenges in the actual operation of the conveyor belt alignment. Mastering these basic steps and paying attention to avoiding common misunderstandings will greatly improve work efficiency and ensure the smooth operation of the conveyor belt.
4.1 Preparation: Tools, Safety and Preliminary Inspection
Before starting the alignment, make sure that the necessary tools such as theodolite,Surveyor’s level, Caliper, etc. are prepared and confirmed that these tools have no errors. At the same time, safety inspection is also very important to ensure that the work area is clean and free of obstacles and safety hazards.
Some people may think that this is unnecessary, but if you ignore the preliminary inspection at this stage and go directly to the adjustment. Doing so will lead to missing potential problems, such as damage to the rollers or support frames, which will affect the subsequent alignment effect. Therefore, it is recommended to check the integrity of all components first to ensure that there are no faults or abnormalities.

4.2 Ensure the roller level
The levelness of the roller directly affects the alignment of the conveyor belt. Use a level to check each roller to ensure that they are on the same level. Many operators overlook details during inspection, such as placing the level at only one point for measurement, while ignoring the length or angle inconsistency of the roller. To avoid this error, it is recommended to measure at multiple locations on the roller to ensure comprehensiveness.
Tip: For extra-long conveyor lines, sometimes each level of roller is divided into three pieces and placed at an angle on both sides, and the middle part is placed horizontally. It is necessary to adjust the standard and method of horizontal measurement by yourself.
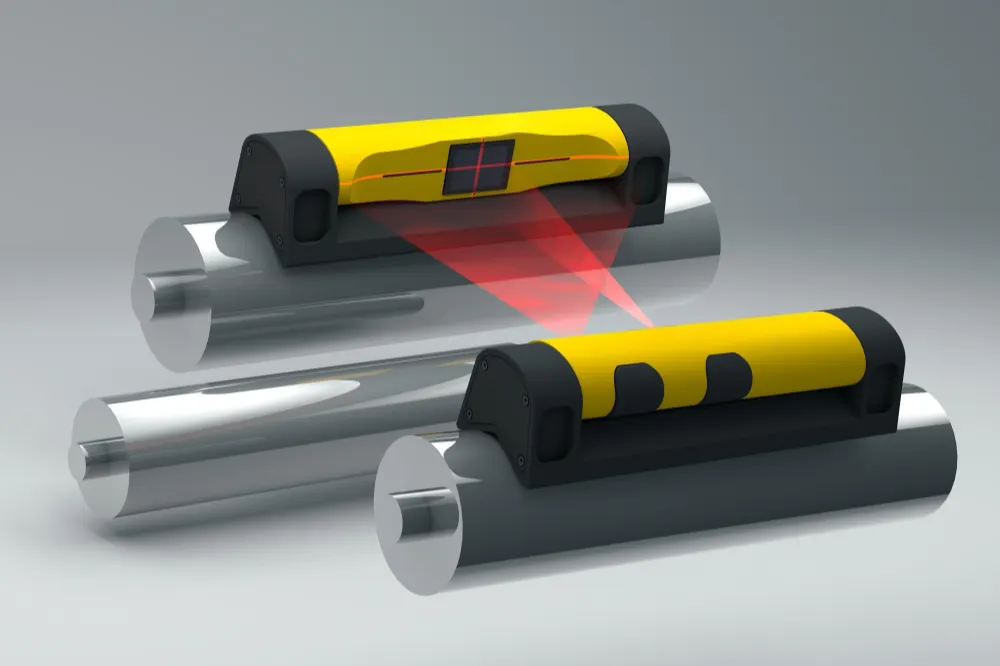
4.3 Determine the center line of the conveyor belt
The center line alignment of the conveyor belt is crucial. Use a theodolite to check whether the conveyor belt is in the center of the equipment. Some operators may directly use visual inspection to determine whether the conveyor belt deviates from the center line. This may be a good method for experienced experts. However, this method is usually prone to errors, resulting in actual deviations that cannot be discovered in time. It is recommended to use an accurate theodolite to accurately locate the center line of the conveyor belt to avoid visual errors.
4.4 Adjust the alignment of the head and tail rollers
Adjusting the alignment of the head and tail rollers is an important part of ensuring the smooth operation of the conveyor belt. A common mistake is to focus only on one end of the head or tail roller without checking whether both ends are fully aligned. To avoid this misunderstanding, use a level and theodolite to fully check the alignment of the head and tail rollers to ensure that they are completely parallel to avoid conveyor belt running problems caused by deviations. Laser alignment systems are recommended for long transport lines.

4.5 Adjust the tension rollers
The tension rollers control the tension of the conveyor belt. Many operators may only focus on the degree of tension when adjusting the tension rollers, but ignore the parallelism of the tension rollers and the conveyor belt. If the tension roller angle is incorrect, it will cause uneven tension on the conveyor belt, which will affect the smooth operation of the belt. When adjusting, make sure that the tension rollers remain horizontal and parallel to the conveyor belt to ensure that the tension is evenly distributed.

4.6 Check and test run after completion
After all adjustments are completed, perform a comprehensive inspection and a short test run. Some operators will ignore the state of the conveyor belt after startup and fail to detect small problems in the initial operation in time. At this time, it is recommended to run at a low speed for a longer time to observe whether the belt is stable and check for irregular wear or offset.

4.7 Detailed Adjustment: Friction Check and Temperature Monitoring
When the conveyor belt is running, pay special attention to the friction and temperature. Uneven friction on both sides of the conveyor belt may cause heat accumulation in the equipment, resulting in early wear of the rubber surface. Use an infrared thermometer to check the operating temperature of the conveyor belt to ensure that the temperature is within the normal range. If the local temperature is found to be too high, it may indicate excessive friction or component wear. Adjust the distance between the conveyor belt and the roller in time.
5. “CIA” rule: an effective way to improve conveyor belt alignment accuracy
Proper conveyor belt alignment is the key to ensuring the efficient operation of the conveyor belt system, and the “CIA” rule provides a simple and practical framework for daily conveyor belt alignment. CIA stands for three steps: CLEAN, INSPECT, ADJUST. Through these three steps, you can effectively manage the alignment of the conveyor belt in daily operations, extend the service life of the conveyor belt, reduce the risk of conveyor belt failure, and improve production efficiency.
5.1 CLEAN: Start with cleaning
Cleaning is the first step to keep the conveyor belt aligned accurately and extend the service life of the conveyor belt. During long-term operation, the conveyor belt will accumulate dust, grease and other impurities, which will affect the normal operation of the conveyor belt and may cause alignment problems. To effectively solve this problem, you can take the following methods:
- Manual cleaning: Use a soft brush, vacuum cleaner and cloth to wipe the surface of the conveyor belt to remove dust, oil and debris attached to the belt surface.
- High-pressure air: For small debris that is difficult to remove, high-pressure air can be used to blow the conveyor belt, especially around the edges of the conveyor belt and the rollers.
- Special cleaning agent: Use non-corrosive cleaning agents to clean the surface of the conveyor belt to avoid damaging the material of the conveyor belt. It is more efficient to choose a special industrial cleaning agent, especially when dealing with oil or sticky substances.
- Automatic cleaning system: For some large systems, you can consider installing an automatic cleaning system to regularly remove debris from the conveyor belt through mechanical brushes or scrapers to reduce the frequency and workload of manual cleaning.
By regular cleaning, you can keep the conveyor belt clean and avoid misalignment caused by dirt accumulation.

5.2 INSPECT: Regularly check the wear of the conveyor belt
Regular inspection is a key link to ensure that the conveyor belt remains in good alignment for a long time. It is usually recommended to conduct a comprehensive inspection once a month, especially under high load or long-term operation, the inspection frequency should be increased. Pay attention to the following aspects:
- Conveyor belt wear: Observe the surface of the conveyor belt for obvious wear marks, especially in high friction areas. If the surface is damaged, cracked or severely worn, it should be replaced in time.
- Pulley and roller inspection: Pulleys, rollers and tensioners are important components of conveyor belt alignment. Check whether these components are excessively worn, corroded or deformed. Replace it in time if there is any problem.
- Belt tension check: Check whether the conveyor belt is too tight or too loose. A loose conveyor belt is prone to slippage or deformation, while a tight conveyor belt will increase the system load and accelerate the wear of the conveyor belt.
Inspection frequency:
- Daily inspection: For conveyor belt systems that are frequently operated, it is recommended to perform basic inspections every day, especially on the conveyor belt surface and edges. Check for wear, cracks or foreign objects stuck.
- Monthly in-depth inspection: Perform an in-depth inspection of the conveyor belt once a month to check the wear of components such as pulleys, rollers and tensioners. Check the belt surface for signs of wear or uneven wear, and whether there is a risk of breakage.
- Quarterly inspection: Perform a comprehensive inspection every quarter to evaluate the overall condition of the conveyor belt, drive system and tensioner. For conveyor belts that are used intensively, this inspection cycle can be shortened.

5.3 ADJUST: Fine adjustment to keep the conveyor belt aligned
Even with regular cleaning and inspection, the alignment of the conveyor belt may change over time and changes in usage conditions. At this time, it is particularly important to accurately adjust the conveyor belt position and tension. Use specialized conveyor belt alignment tools, such as alignment indicators, laser alignment equipment, etc., to ensure the accuracy of each adjustment and avoid unnecessary repetitive operations. Pay special attention to checking every link of the conveyor belt during adjustment to ensure that there is no deviation and keep the conveyor belt running smoothly.
By applying the CIA principle, you can not only effectively manage the alignment status of the conveyor belt, but also avoid conveyor belt failures caused by improper alignment through preventive maintenance, ensure the smooth operation of the conveyor belt system, and improve production efficiency.

6. Importance of conveyor belt alignment
Ensuring conveyor belt alignment is key to ensuring your equipment operates efficiently and for long periods of time. A simple alignment issue can have serious consequences if ignored. Therefore, understanding and implementing correct alignment methods is crucial for any production line.
6.1 Reduce wear and extend equipment life
Proper belt alignment can significantly reduce belt friction and wear, extending the life of your equipment. According to an industry study, keeping conveyor belts aligned correctly can reduce wear by up to 50%, avoiding premature replacement and high maintenance costs. In addition, avoiding abnormal operation caused by conveyor belt misalignment can also reduce the failure rate of the entire system, thus greatly improving production efficiency.
6.2 Prevent the conveyor belt from deflecting and ensure safety
Conveyor belt misalignment is one of the most common problems with poor alignment. Offset not only reduces production line efficiency, but may also cause operational safety issues. If the conveyor belt deviates from the track, it will cause materials to fall and even damage other equipment. Maintaining the correct alignment of the conveyor belt can effectively prevent this from happening and ensure the safety of operators and equipment.
6.3 Improve production efficiency and reduce downtime
Conveyor belt downtime and maintenance often result in reduced productivity. According to data, proper conveyor belt alignment can reduce equipment downtime by up to 30%. If the alignment of the conveyor belts can be regularly checked and adjusted, the production line will run more smoothly, thereby improving overall work efficiency.
6.4 Reducing costs through better alignment methods
Good alignment not only improves productivity but also reduces operating costs. According to studies, proper conveyor belt alignment reduces the energy consumption of the system, as improper alignment increases friction, resulting in increased power consumption. A precisely aligned conveyor belt can reduce power consumption by more than 30% and reduce unnecessary energy waste. This approach is not only environmentally friendly, but also effectively saves costs.
6.5 Improve material handling and improve logistics efficiency
Well-aligned conveyor belts can improve material handling efficiency and ensure the stability of materials during transportation. The accuracy of material handling is directly related to the efficiency of the production line, especially in high-demand industries such as food processing, mining and chemicals, where any small deviation may lead to big problems in production. Reasonable alignment can ensure smooth transportation of materials and reduce the possibility of material jamming, thereby improving the stability and efficiency of the entire production process.
6.6 Dealing with the challenges of long conveyor belt alignment
Alignment of long-distance conveyor belts is particularly complex because the conveyor belts travel a long distance and are easily affected by environmental factors such as temperature changes, humidity and load. Therefore, regular inspection and fine adjustment are particularly important for long-distance conveyor belts. In this case, the use of professional alignment tools and techniques can effectively solve the alignment problem of conveyor belts during long-distance transportation and maintain the smooth operation of the equipment.

6.7 Prevent equipment overload and improve operational stability
If conveyor belt alignment issues are not addressed in a timely manner, the conveyor belt and related equipment will be subject to additional loads. For example, when a conveyor belt goes astray, the drive needs to work harder to compensate for this deviation, which can lead to motor overload or even failure. Research shows that the energy consumption of a conveyor system that operates in a misaligned state for a long time will increase by more than 20%, and the overload of the motor may shorten its service life. Regular alignment inspection of the conveyor belt can effectively reduce the burden on the equipment, ensure the stable operation of the conveyor belt and drive device, and avoid excessive wear.
6.8 Ensure the accuracy of material transportation and avoid deviations causing production line disorder
The alignment of the conveyor belt not only affects the health of the equipment and belt, but also directly affects the conveying accuracy of the material. If the conveyor belt deviates, the materials may deviate from the predetermined trajectory, causing material accumulation and jamming, and even affecting the overall operation of the production line. In a production environment with high precision requirements, the accuracy of material transportation is crucial. For example, in the fields of food processing or pharmaceutical production, material deviation may lead to contamination or substandard products during the production process, causing serious losses. Studies indicate that correctly aligned conveyor belts can significantly reduce material errors and ensure a smooth and safe production process. This precision guarantees production efficiency and reduces the risk of incorrect material transport.
7. Solve Common Belt Alignment Problems
7.1 How to Solve Belt Misalignment Problems?
Belt misalignment is often associated with poor roller alignment or uneven belt tension. The key to solving this problem is to accurately align the belt and rollers. Use a laser alignment tool regularly to check that the rollers are parallel to the belt, especially the drive and tail rollers. Adjust the roller position as needed to align with the belt centerline. Make sure the roller surface is smooth and free of dirt or wear to reduce friction on the belt and prevent misalignment.
7.2 How to Prevent Conveyor Belt Edge Wear?
Edge wear is often caused by the belt running off track or uneven belt tension. To prevent excessive wear, regularly adjust the belt tension to evenly distribute it and avoid excessive pressure on either side. If the wear is caused by the belt running off track, it can be solved by adjusting the guide wheels. In addition, using more wear-resistant belt materials, such as adding reinforcement layers or choosing a belt designed for high-wear environments, can also effectively extend the service life.

7.3 How to Prevent Drive Roller Slippage?
Drive roller slippage is usually related to insufficient belt tension or wear on the drive roller surface. Make sure there is no oil or debris on the drive roller surface, which will reduce friction and reduce drive efficiency. Increase the tension of the drive roller, but avoid over-tensioning that will damage other parts. At the same time, using roller lining materials with higher friction, such as rubber or silicone coatings, can effectively prevent drive roller slippage. Regularly check the surface condition of the drive roller and replace worn parts in time.
7.4 How to deal with the impact of environmental factors on conveyor belt alignment?
Conveyor belts are prone to alignment problems in hot, cold, humid or dusty environments. Use protective covers to reduce the impact of environmental pollution on conveyor belts, especially when handling hot materials, and choose conveyor belts with strong high temperature tolerance. If the environment is too humid, use waterproof materials or coatings to avoid contact between the conveyor belt and moisture. For dusty factories, installing an automatic cleaning system can help keep the conveyor belt and roller surface clean and avoid dust accumulation that causes alignment problems.
7.5 How to deal with roller liner wear?
Wear of the liner directly affects the smooth operation of the conveyor belt. Regular inspection of the wear of the roller pads is key. If the pads are found to be deformed or severely worn, they should be replaced as soon as possible. Using roller pads made of highly wear-resistant materials can effectively increase the service life of the pads and reduce the need for frequent replacement. Regularly check and clean the rollers to ensure that they are free of excessive dust or adhesion, which will cause premature damage to the pads.
7.6 How to prevent conveyor belt fatigue and aging?
Conveyor belt fatigue and aging is a long-term accumulation problem, usually manifested as cracks, deformation or surface discoloration. To prevent fatigue and aging, the appropriate material should be selected according to the working conditions of the conveyor belt. For example, for special environments such as high strength and high temperature, use more wear-resistant and high-temperature resistant composite materials. During use, regularly check the surface of the conveyor belt and replace it in time if cracks or local wear are found. Reasonably arrange maintenance cycles and replace them periodically according to the frequency of use to prevent performance degradation caused by aging.

8. Solutions when belt alignment problems occur
If the above methods still cannot solve your belt alignment problem, you can also find more solutions in the following ways.
8.1 Reliable belt troubleshooting resources
When you encounter belt alignment problems, you first need to rely on professional equipment manuals and manufacturer support to find solutions. In addition, you can use industry professional books or online courses to learn more professional knowledge and improve your understanding of belt maintenance. If conditions permit, contacting the equipment supplier’s technical support team is also a reliable solution. They can provide customized guidance and support based on specific circumstances.
In addition to the information provided by the manufacturer, third-party technical service companies are also a powerful resource choice. These companies usually have more experience and can provide professional solutions for various complex problems. If the problem is more complex, or the alignment deviation has affected production efficiency, finding a technical support team for on-site inspection and adjustment will undoubtedly solve the problem more quickly and accurately.
8.2 Seek professional alignment support
For some complex belt alignment problems, self-repair may not be effective enough. In this case, it is particularly important to invite professional technicians to conduct on-site inspections and adjustments. Professionals usually use high-precision tools (such as laser alignment instruments) to ensure the accuracy of conveyor belt alignment. They can not only quickly identify the root cause of the problem, but also provide professional adjustment solutions in a short time.
In addition, regular maintenance services are also a guarantee to ensure the long-term and efficient operation of the conveyor belt system. Many conveyor belt suppliers or professional maintenance companies provide regular maintenance contracts to regularly check the alignment status of the conveyor belt and make necessary adjustments. This practice helps to detect potential problems in time and prevent small problems from turning into major failures that affect the normal operation of the production line.

9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Conveyor Belt Alignment
Many users will encounter some common problems when operating conveyor belts. To address these concerns, we will provide detailed answers and solutions to several high-frequency problems below.
9.1 How to fix conveyor belt alignment problems?
Conveyor belt alignment problems are usually caused by uneven tension, improper position of guide wheels, or wear on the conveyor belt surface. To fix alignment problems, you can follow the following steps:
- Adjust the guide wheels: Make sure the guide wheels are properly aligned. Check whether the guide wheels are offset and adjust the angle or position appropriately so that they can properly guide the conveyor belt.
- Equally adjust the tension: Uneven tension is an important reason for conveyor belt deviation. Check the tension system to ensure that the tension is evenly distributed on both sides of the conveyor belt. Fix uneven problems by adjusting the tension device.
- Check and replace worn parts: If the rollers, guide wheels and other parts are severely worn, they should be replaced in time. Worn parts can cause conveyor belt deviation or increased friction, affecting alignment accuracy.
- Clean the conveyor belt: Clean the debris, oil and dust on the conveyor belt, which may cause the conveyor belt to run unstably and increase the risk of deviation.
By following these steps, you can greatly improve the alignment of your conveyor belt and ensure smooth operation of your equipment.
9.2 What are the best tools for conveyor belt alignment adjustment?
When aligning your conveyor belt, it is important to use the right tools. Here are some common tools:
- Laser aligner: Laser aligners are high-precision tools that can help detect the alignment between the conveyor belt and the rollers. The laser beam allows you to accurately know if the conveyor belt is deviating.
- Tension meter: Used to measure the tension of the conveyor belt to ensure that the tension on both sides is balanced, thus avoiding alignment problems caused by uneven tension.
- Plumb line and level: In the absence of a laser aligner, using a plumb line and level to check the straightness and parallelism of the conveyor belt is also a practical solution.
- Tape measure and caliper: By measuring the width of the conveyor belt and the distance between the support frame and the roller, check for any deviation and help detect alignment problems in time.
Choosing the right tool for your needs can effectively improve the alignment accuracy and avoid deviations caused by human errors.
9.3 How often should the conveyor belt alignment be checked?
Regularly checking the alignment of the conveyor belt can help extend the life of the equipment and improve production efficiency. It is recommended to conduct inspections at least once a month, especially under high load or high speed conditions. If the conveyor belt is running in a humid and dusty environment, the inspection frequency should be increased appropriately.
If the conveyor belt is found to be offset or abnormal noise, increased friction, etc. is found during production, it should also be inspected and adjusted immediately. Timely detection and repair of problems can effectively avoid more serious damage and reduce downtime.
9.4 How to keep the conveyor belt centered and aligned?
In order to keep the conveyor belt centered and aligned, the following measures can be taken:
- Install an automatic center adjustment device: Some modern conveyor belt systems are equipped with an automatic center adjustment device that can monitor the position of the conveyor belt in real time and automatically adjust it to ensure that the conveyor belt is always centered.
- Regularly adjust the tension system: Ensure that the tension on both sides of the conveyor belt is evenly distributed. Uneven tension may cause the conveyor belt to deviate to one side, which can be effectively solved by adjusting the tension system.
- Regularly check the rollers and guide wheels: Check whether these key components are worn. If asymmetrical wear occurs, replace or repair them in time to avoid alignment problems caused by equipment failure.
- Clean the conveyor belt surface: Keep the conveyor belt surface clean to avoid the accumulation of dirt, grease and other debris, which may cause the conveyor belt to deviate and affect normal operation.
Taking these preventive measures can greatly reduce the deviation of the conveyor belt and improve the stability and operating efficiency of the equipment.

















