1.The Importance of Finding Reliable Suppliers of Conveyor Belts
Finding reliable suppliers of conveyor belts is essential to ensure the smooth operation of production lines and maintain efficiency across various industries. Whether you are in mining, logistics, or food processing, the right conveyor belt supplier can significantly impact your overall productivity and operational costs.
A trustworthy supplier will not only provide high-quality products but also offer timely support, customized solutions, and flexible order options that meet your specific requirements. In a fast-paced global market, reliability, quick response times, and cost-effectiveness are crucial when sourcing conveyor belts.
Selecting the right supplier involves understanding their expertise, product offerings, and ability to meet industry standards. By partnering with experienced suppliers, businesses can avoid downtime, reduce operational risks, and ensure the longevity of their production processes. This guide highlights key factors to consider when choosing a supplier for your conveyor belt needs, helping you make an informed decision that benefits your business in the long term.

2. Common Conveyor Belt Types and Their Applications
The following is a brief introduction to some common conveyor belt types and their specific applications.
2.1 Rubber conveyor belt
Rubber conveyor belt is one of the most common types of conveyor belts in industrial applications, known for its excellent wear resistance and impact resistance. It is usually made of high-strength natural or synthetic rubber materials and is suitable for transporting heavy materials. It is mainly used in heavy industries such as mining, coal, metallurgy and steel manufacturing. The production environment of these industries is usually very harsh, and conveyor belts with extremely high tensile strength and high temperature tolerance are required to ensure stable operation under long-term high loads.

Advantages:
High tensile strength: Can withstand large loads and heavy material impact.
Wear and impact resistance: Especially suitable for transporting sharp and highly abrasive materials.
Superior performance and long service life: Excellent performance in harsh working environments and low long-term maintenance costs.
Disadvantages:
Heavy weight: The high density of rubber materials increases installation and maintenance costs.
Easy to absorb dust: Not suitable for environments that require frequent cleaning and light load applications, and dirt and dust are easily accumulated on the surface.
Material Type | Tensile strength range (MPa) | Remark |
NR | 8 – 12 | Suitable for general industrial applications at low cost. |
SBR | 10 – 14 | Good abrasion resistance, suitable for medium loads. |
5 – 15 | Excellent high temperature resistance, suitable for high temperature environments. | |
FKM | 10 – 18 | Excellent chemical and high temperature resistance, suitable for harsh environments. |
IIR | 6 – 10 | Good air tightness and chemical resistance, suitable for special applications. |
PU Reinforced Rubber | 15 – 25 | High tensile strength for heavy duty and high strength applications. |
2.2 PVC/PVG conveyor belts
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) and PVG (polyvinyl chloride impregnated rubber) conveyor belts are lightweight and flexible conveyor belts widely used in light material transportation. These conveyor belts have good oil, chemical and water resistance, and are particularly suitable for industries with high environmental cleanliness requirements, such as food processing, pharmaceutical and packaging industries. PVC conveyor belts are mainly used for flat transportation, while PVG conveyor belts are suitable for inclined transportation due to their double-sided coating, which provides better sliding and wear resistance.

Advantages:
Lightweight: easy to install and operate, significantly reducing the energy consumption of equipment.
Economical: Compared with other types of conveyor belts, PVC/PVG conveyor belts have lower material and maintenance costs.
Oil and chemical resistant: particularly suitable for industries exposed to oils and chemicals, such as food processing and pharmaceutical industries.
Easy to clean: smooth surface prevents material residue and contamination.
Disadvantages:
Poor high temperature resistance: not suitable for high temperature environments, high temperature will cause material deformation or decomposition.
Not suitable for heavy material transportation: Due to the soft material, it is more suitable for the transportation of light to medium materials, but not for long-distance heavy material transportation.
| Material Type | Tensile strength range (MPa) | Remark |
| PVC | 6-12 | Economical for light to medium loads. |
| PVG | 8-15 | Provides improved sliding and wear resistance for inclined transportation. |
| Oil-resistant PVC | 10-18 | Suitable for use in oily environments for improved abrasion resistance. |
| Double-sided PVC | 8-14 | Provides double-sided wear resistance for improved transport stability. |
| Reinforced PVC | 12-20 | Improves tensile strength by adding steel wire or fiber reinforcement. |
2.3 PU (Polyurethane) Conveyor Belt
PU (Polyurethane) conveyor belts are particularly suitable for industries that require extremely high hygiene and safety standards, such as food processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing, due to their excellent wear and tear resistance. Such conveyor belts meet food grade standards and are suitable for environments that require strict cleaning conditions. Compared with PVC conveyor belts, PU conveyor belts perform better in oil and chemical resistance and are suitable for transporting oily and fatty materials.
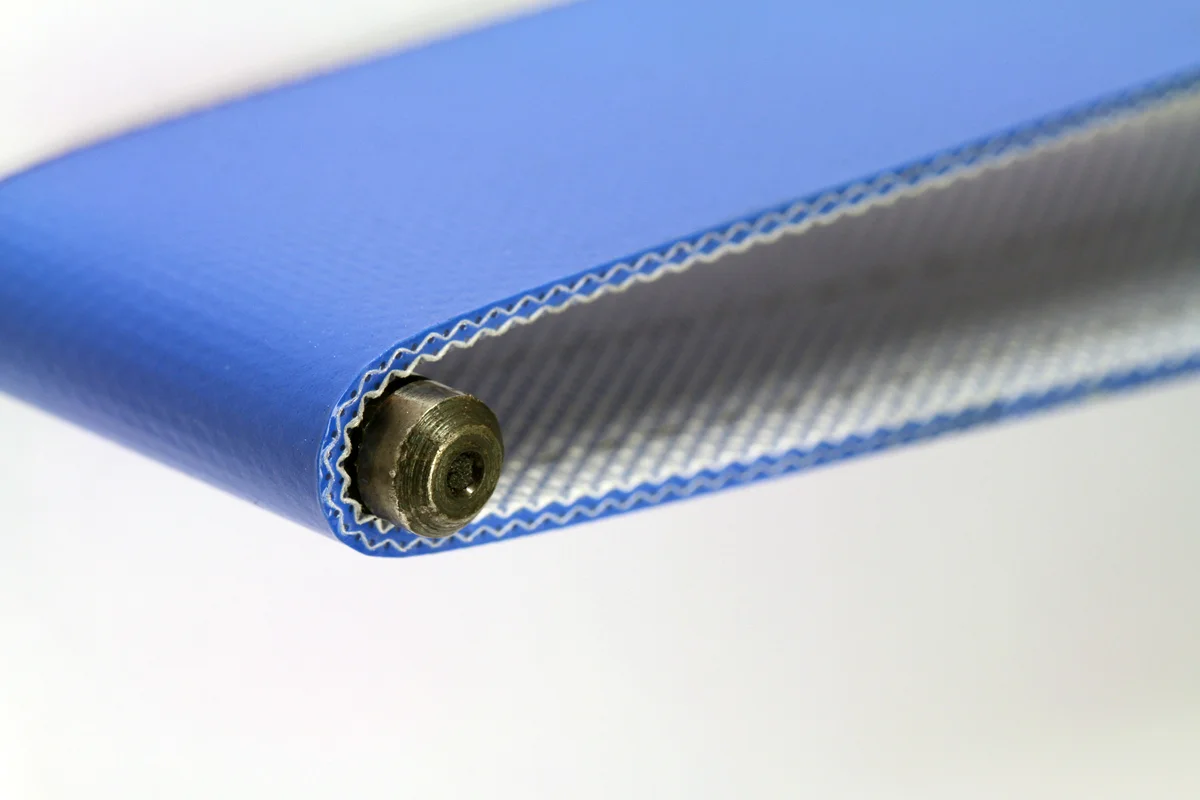

Advantages:
High wear and tear resistance: Suitable for frequently used conveyor systems, the tensile strength of PU materials is usually higher than that of rubber.
Food grade certification: It does not contain toxic substances and can directly contact food, meeting the hygiene requirements of the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Oil and chemical resistance: It can be used in environments containing corrosive substances, such as grease and chemicals, and is not easily contaminated.
Easy to clean and maintain: The smooth surface facilitates the removal of adhesives and is suitable for production environments with strict hygiene standards.
Disadvantages:
Higher cost: Compared with PVC or rubber conveyor belts, PU conveyor belts have higher material and production costs.
Not suitable for heavy materials and high temperature environments: Although PU materials have a wide temperature tolerance range, they are easy to deform or degrade in extremely high temperature environments, which limits their use in certain high temperature occasions.
| Material Type | Tensile strength range (MPa) | Remark |
| PU | 15 – 25 | High tensile strength for heavy-duty and high-strength applications. |
| Food-grade PU | 18 – 30 | Conforms to food safety standards and is suitable for food processing. |
| Chemical-resistant PU | 20 – 28 | Resistant to acids, alkalis and organic solvents for the chemical industry. |
| High-temperature PU | 17 – 26 | Suitable for high temperature environments such as baking and drying processes. |
2.4 Metal Wire conveyor belts
Metal conveyor belts are usually made of corrosion-resistant metals such as stainless steel and carbon steel, and are widely used in extreme environments and high-intensity industrial operations. Due to their high strength, high temperature and corrosion resistance, these conveyor belts are often used in occasions where heavy loads and high temperatures need to be transported, such as baking and roasting equipment in food processing, the chemical industry, metal processing, and high-temperature processing equipment.

Advantages:
Excellent high temperature resistance: Metal conveyor belts can withstand temperatures up to 800°C or higher and are suitable for high-temperature processing equipment such as ovens, dryers, and heat treatment equipment.
Strong corrosion resistance: Materials such as stainless steel and galvanized steel have good corrosion resistance and are suitable for applications that come into contact with corrosive substances such as acids and alkalis.
High strength and wear resistance: The tensile strength and hardness of metal conveyor belts are much higher than other materials, and they can withstand heavy materials and mechanical stress, extending their service life, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs.
High stability and safety: In high temperature or chemically corrosive environments, metal conveyor belts provide a stable and safe transmission path, and are not prone to risks caused by material aging or degradation.
Disadvantages:
Heavy weight and complex installation: Metal conveyor belts are heavier, and installation and maintenance usually require more labor and time, increasing initial investment and operating costs.
High cost: Manufacturing and material costs are higher than other materials, and are not suitable for applications with limited budgets.
| Material Type | Tensile strength range (MPa) | Remark |
| Stainless Steel Belt | 30 – 50 | High strength for high temperature and corrosive environments. |
| Carbon Steel Belt | 25 – 45 | High strength for heavy duty and high wear applications. |
| Galvanized Steel Belt | 28 – 48 | Features an additional corrosion-resistant layer for corrosive environments. |
| Aluminum Alloy Belt | 20 – 35 | Lightweight but moderately strong for high temperature environments where light weight is required. |
| Copper Belt | 22 – 40 | Good corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity for specific industrial applications. |
2.5 Modular plastic conveyor belts
Modular plastic conveyor belts are composed of interlocking plastic modules, usually made of engineering plastics such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE) or polyamide (PA), and are highly adaptable and flexible. Designed for easy maintenance and cleaning, the modules can be easily removed and replaced, suitable for applications that require frequent cleaning or maintenance.
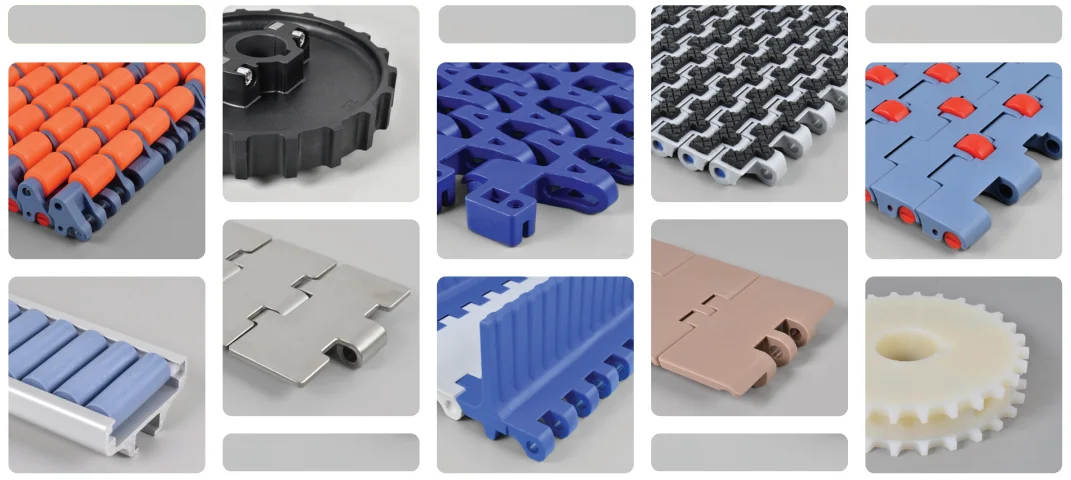
Advantages:
High flexibility: The modular design allows the conveyor belt to adapt to complex transmission paths, such as bends and tilt angles. For example, PP modules work reliably in the range of -10°C to +60°C, and PE modules can even be used below -40°C.
High chemical resistance: Plastic modules have excellent chemical resistance and are suitable for contact with cleaning agents and disinfectants. PP materials have good resistance to acids, alkalis and organic solvents.
Low maintenance costs: Due to the modular structure, damaged modules can be replaced individually, reducing overall maintenance costs. According to some manufacturers, the use of modular conveyor belts can reduce maintenance downtime by more than 50%.
Easy to clean: The smooth surface prevents material residue and effectively meets the strict hygiene requirements of the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Disadvantages:
Not suitable for heavy load or high temperature applications: Plastic materials have limited tensile strength and high temperature tolerance. For example, the maximum tensile strength of PP is about 30 MPa, which is much lower than that of metal materials and is not suitable for long-distance transportation of heavy loads or use in high temperature environments.
Insufficient durability in some extreme environments: In high-impact or high-abrasion environments, plastic modules may wear or crack quickly and are not suitable for continuous high-stress working environments.
| Material Type | Tensile strength range (MPa) | Remark |
| PP Modular Belt | 10-18 | Suitable for light to medium loads, with good chemical resistance. |
| PE Modular Belt | 12-20 | Suitable for applications requiring high flexibility and chemical resistance. |
| PA Modular Belt | 14 – 22 | Excellent wear resistance and tensile strength, suitable for high load applications. |
| High-strength PP | 16 – 25 | Enhanced tensile strength, suitable for medium to high load applications. |
| Chemical-resistant PP | 15 – 23 | Suitable for the chemical industry, resistant to acids, alkalis and organic solvents. |
4. Suppliers of Conveyor Belt Selection:Key Considerations
Choosing the right conveyor belt is key to ensuring that your production line runs efficiently. Different types of conveyor belts have different characteristics in terms of materials, design, and functions. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing a conveyor belt.
4.1 Application Requirements
First, it is necessary to clarify the requirements of the conveyor belt based on the application scenario. Different materials (such as heavy objects, food, or chemicals) require different conveyor belt materials. Understanding the size, weight, temperature, and environmental conditions (such as humidity, corrosiveness, etc.) of the material is the first step in choosing the right conveyor belt.
4.2 Conveyor Belt Size and Specifications
The size and specification of the conveyor belt determine its adaptability in the production line. The appropriate width, length, and thickness need to be selected based on the size of the material, the layout of the production line, and the complexity of the transport path (such as whether it needs to bend or tilt). Make sure that the conveyor belt can stably carry the material and match the layout of the production line.
4.3 Material Selection
Common conveyor belt materials include rubber, PVC, PU, and metal. Rubber conveyor belts are suitable for heavy material transportation and have strong wear resistance; PVC conveyor belts are suitable for light load applications and are economical; PU conveyor belts are suitable for food processing and meet hygiene requirements; metal conveyor belts are resistant to high temperatures and suitable for harsh environments. Choosing the right material according to production needs can extend the service life of the conveyor belt and improve transportation efficiency.
4.4 Consider durability and maintenance
Choosing a durable conveyor belt can reduce downtime and long-term maintenance costs. Although the initial cost of materials with high tensile strength and good wear resistance is higher, they can reduce frequent replacement and maintenance, bringing better long-term economic benefits.

4.5 Cost and budget
When purchasing a conveyor belt, it is necessary to consider not only the initial purchase cost, but also its long-term maintenance cost. Although the price of a high-quality conveyor belt is higher, it will be more cost-effective in the long run due to its strong durability and reduced replacement and maintenance costs.
5. Key factors when purchasing a conveyor belt
When purchasing conveyor belts, there are several key factors to consider to ensure that the product selected meets the needs of the particular application and provides optimum performance and value for money.
5.1 Quality and durability of the conveyor belt
Quality is one of the most important factors when selecting a conveyor belt. A quality conveyor belt will provide a longer service life with fewer breakdowns and less maintenance. Check the parameters of the conveyor belt to ensure that it has adequate abrasion, heat, corrosion and UV resistance, which will directly affect the performance of the belt in harsh environments.
5.2 Supplier’s reputation and service
It is very important to choose a supplier with good reputation and rich experience. A professional supplier can not only provide high-quality products, but also pre-sales consulting, customized services and perfect after-sales support. During the procurement process, learn about the supplier’s response speed, delivery time and maintenance services to ensure worry-free maintenance.

5.3 Balancing Cost and Budget
Although price is a key factor in purchasing decisions, it is important not to look only at price and ignore quality and long-term costs. Some low-priced conveyor belts may appear to save money in the short term, but frequent replacement and maintenance costs keep piling up, leading to more hidden expenses instead. Reasonable balance between initial investment and long-term usage cost is a wise purchasing strategy.
5.4 Customized Requirements
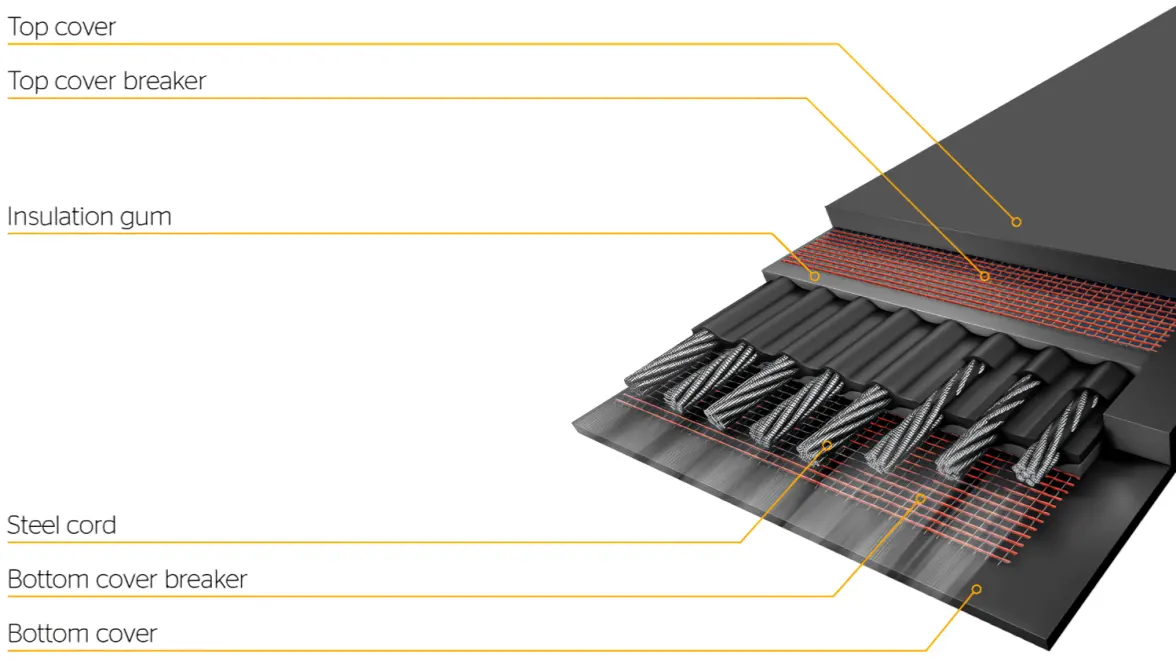
Some industries have specific requirements for total belt thickness, core material (EP / ST), top cover thickness and bottom cover thickness, which makes customized service especially important. Ensure that your supplier can provide a customized solution to your specific needs to ensure that the belts provide the best performance in the particular application.
5.5 Environmentally friendly and safe
As environmental awareness increases, many companies consider the environmental friendliness of their conveyor belts when purchasing them. For example, choosing materials that meet environmental standards ensures that no harmful substances are released during the use of the belt. In addition, the safety of a conveyor belt should not be overlooked to ensure that it does not pose a safety risk to operators and equipment during transportation.

6. Cross-border export guide: trade terms and important considerations
When sourcing conveyor belts across borders, it’s vital to understand the terms of international trade and the associated export requirements. This ensures that unnecessary disputes are avoided and that the transaction runs smoothly.
6.1 Common International Trade Terms
International trade terms (Incoterms) provide a clear allocation of responsibility and definition of risk for buyers and sellers. Common trade terms include:
FOB (Free On Board, port of shipment on board): the seller is responsible for the transportation of goods to the designated port and shipment, costs and risks transferred to the buyer.
CIF (Cost, Insurance and Freight): The seller is not only responsible for transportation costs, but also needs to insure the goods until the port of destination.
EXW (Ex Works): The seller’s place of delivery is usually the seller’s factory or warehouse, and the risks and costs are transferred to the buyer after delivery from the factory.
Choosing the appropriate trade terms can help you clarify your respective responsibilities and cost sharing and avoid transaction disputes.
6.2 Required Export Documents
Cross-border transactions require the preparation of a number of necessary documents to ensure that the goods can pass through customs smoothly. Common import documents include:
Commercial invoice: setting out the name, quantity, unit price and total amount of the goods.
Packing List: detailing the packaging of the goods.
Form E: proves the origin of the merchandise and can sometimes be the key to tariff concessions.
Ensuring that these documents are fully prepared not only speeds up the shipping process, but also avoids customs issues.
6.3 Tariffs and Tax Policies
Different countries and regions impose different tariffs and taxes on imported goods. Tariff rates usually depend on the category, value and origin of the goods. Knowing the tariff policies of the markets you are importing into can help to accurately calculate total costs and avoid unexpected additional expenses.
In addition, some countries and regions may offer reduced tariffs or preferential rates for products in specific industries. Work with suppliers to ensure that the appropriate product categories are selected to maximize tariff benefits. Some countries and regions may offer additional tariffs or preferential rates for products in specific industries.

6.4 Certification and Compliance Requirements
For cross-border transactions, many countries have specific quality standards and certification requirements for imported goods, particularly in areas involving food, pharmaceuticals and industrial equipment. Common certifications include:
CE certification: a mark of compliance for products in the EU market.
FDA Certification: Product standards approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
ISO Certification: International Organization for Standardization certification that ensures product compliance with global quality standards.
Ensure that your conveyor belt products meet the certification requirements of your target markets and avoid the legal risks associated with non-compliance.
6.5 Intellectual Property Protection
Cross-border transactions also require consideration of intellectual property protection. Intellectual property laws and enforcement vary greatly from country to country. To avoid infringement of patents, trademarks or copyrights, make sure that your products do not violate the relevant regulations and take the necessary steps, such as signing contractual agreements, registering trademarks, etc.

7. Cross-border logistics: transportation options and challenges
Logistics and transportation for cross-border sourcing is a key component that involves a number of aspects, including time, cost, and mode of transportation. According to different business needs, choosing the right mode of transportation can not only optimize the cost, but also ensure that the goods are delivered on time and safely.
7.1 Transportation Mode Selection
Common cross-border transportation modes include sea transport, air transport and land transport, each of which has its own applicable scenarios and advantages.
Sea transportation: It is suitable for bulk goods, especially those with large volume and weight. The cost of sea transportation is relatively low, but the transportation time is longer. For large orders or goods that need to be transported in bulk, sea transportation is the most economical choice, and it is optimal for rubber conveyor belts to choose this method.
Air Freight: For small items or high value goods that need to be transported urgently. Air freight is faster but more costly. For orders with high timeliness requirements, air freight is the best choice, and this method is the least recommended, except that your budget is very sufficient and you have a very high degree of urgency with this product.
Ground transportation: Suitable for cross-border transportation between neighboring countries. Ground transportation is relatively flexible and suitable for geographically close areas. For markets such as Southeast Asia and Europe, ground transportation is a cost-effective option.
Choosing the right mode of transportation can be determined by a number of factors, including the weight and volume of the goods, the transportation time and the budget.

7.2 Customs and Import Clearance
Each country has its own customs regulations, and importers need to understand the customs policies of the target market to ensure the smooth clearance of goods. The process of customs clearance requires the submission of relevant customs documents, including invoices, packing lists, certificates of origin and so on.
To avoid delays or extra costs caused by customs clearance issues, you can choose to work with an experienced customs clearance agent to ensure that all procedures are carried out in accordance with the regulations. Moreover, knowing the customs clearance process in advance will help to predict the difficulties that may be encountered and make a good plan.
7.3 Logistics cost management
The cost management of cross-border logistics is very important. Transportation costs not only include the cost of goods transportation, but also involve additional costs such as insurance, tariffs, warehousing and so on. Reasonable planning of logistics budget and understanding the cost structure of different modes of transportation will help you optimize the cost and enhance the profit.
Transportation insurance: In order to prevent the loss of goods during transportation, it is recommended to purchase transportation insurance for the goods. The cost of insurance is usually related to the value of the goods, mode of transportation and destination.
Warehousing costs: In some cases, transit warehousing is required during transportation. It is important to know the storage costs in the target market to avoid additional expenses due to storage delays, but from our experience over the years, very few customers encounter this problem.
7.4 Transportation Time
Delivery time is an important reference factor for choosing logistics mode and arranging transportation plan. Quick response and accurate delivery time is the first element in choosing a supplier. You can ask your freight forwarder or supplier to provide you with real-time production process or product positioning every once in a while.

7.5 Challenges of cross-border logistics
Although cross-border logistics facilitates global trade, there are still some challenges in practice:
Transportation delays: Cross-border transportation may experience delays due to customs, weather, labor issues, and other factors. Establishing a long-term relationship with a reliable logistics partner can reduce such risks.
Complex customs policies: Customs policies vary greatly from country to country, and special care is needed, especially when it comes to banned or restricted imported goods.
Handling of unforeseen circumstances: Factors such as natural disasters and changes in the international political environment can lead to transportation disruptions or cost increases. Knowing the relevant information in advance and preparing contingency plans is a guarantee to ensure that the goods will be delivered on time.
8. Global Vision and Industry Coverage
Quality, service and customization are crucial factors when choosing a conveyor belt supplier. Our conveyor belts can meet the different needs of various industries with advanced production technology, strict quality control and flexible customization services. From food processing to mining, chemical, power and other fields, our products have successfully served many companies around the world.
We are well aware that purchasing decisions need to consider many aspects, including cost-effectiveness, delivery time, after-sales support, etc. For this reason, we provide low MOQ flexible procurement solutions and promise to respond quickly to ensure that your needs are solved as quickly as possible. At the same time, we continue to optimize production processes and product design to ensure that we can provide high-quality conveyor belts that meet international standards to help your business achieve efficient and stable operations.
Whether you are a first-time purchaser or a long-term partner, we look forward to working with you. Choosing our conveyor belts, you will get not only product protection, but also a trustworthy long-term partner.


















