In today’s global industrial landscape, selecting the right conveyor belt suppliers is becoming a strategic decision tied to uptime, delivery reliability, and long-term stability. This article outlines the core capabilities that shape modern supply systems, while systematically presenting ten globally representative suppliers and the roles they play in different markets. It further explains how supply-chain maturity, documentation, and engineering support are redefining future procurement models across the conveyor belt industry.
1. Why Choosing Top Conveyor Belt Suppliers is Crucial for Your Business
When sourcing conveyor belts, you’ll discover a reality: many manufacturers and suppliers are simply not on the same level. This isn’t meant to belittle manufacturers; I am one myself, it’s just that we approach problems from different angles.
I previously wrote an article about the top 15 conveyor belt manufacturers in the world, clearly outlining their production capabilities and how to choose them.
As a manufacturer with 20 production lines, Tiantie Industrial, I certainly know how important manufacturers are—we determine whether a product can be manufactured. But if you ask me why so many multinational mines, logistics centers, and power plants ultimately choose large conveyor belt suppliers instead of individual manufacturers, the answer is simple:
Manufacturers provide the product; suppliers provide the “guarantee.”
Suppliers not only provide you with conveyor belts, but also inventory, delivery times, on-site support, international standard documentation, global logistics, B2B customization, stock selection, after-sales response… These determine whether your system can operate stably 24/7.
In other words: You rely on the manufacturer’s “production capacity,”
but you rely on conveyor belt suppliers for their “ability to keep the system running smoothly.”

1.1 In modern industrial systems, suppliers are a more critical link than the manufacturing end.
Excellent conveyor belt suppliers play the role of “invisible infrastructure” in your production chain. They are not only responsible for delivery, but also for:
- Matching operating conditions, structural selection, and abrasion resistance level recommendations (Tiantie Industrial can currently do all of these)
- Material review and international compliance (DIN, ISO, RMA, CSA)
- Customized production and technical integration
- Inventory preparation + global shipping scheduling
- Project delivery cycle control and risk management
Simply put, the higher your production efficiency, the greater the challenge to your suppliers and supply chain.
Relying on stable conveyor belt suppliers keeps your system “alive,” rather than shutting down waiting for the next shipment. However, many mine engineers now begin procurement planning well in advance of the next cycle.
1.2 The global conveyor belt market is experiencing accelerated growth, further amplifying the value of suppliers.
Industrial automation is driving continuous growth in conveyor belt demand. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global conveyor belt market will reach USD 7.2 billion by 2028 (Source:Fortune Business Insights).
Several key drivers are behind this growth:
- Expansion of e-commerce and smart logistics
- Accelerated infrastructure and mining projects
- Increased conveyor belt configuration in automated production lines
- Upgrades in material technology (e.g., upgrades in heat resistance, low energy consumption, and flame-retardant structures, passively increasing conveyor belt lifespan).
These factors make the inventory capacity, delivery speed, and technical support of high-performing suppliers more critical than ever before, and are gradually increasing the importance of high-quality rubber conveyor belt suppliers in global sourcing.
1.3 Why do different regions have completely different requirements for suppliers?
Does your region determine whether your suppliers are “good enough”?
- Southeast Asia: High concentration of rare metal mines and large demand for conveyor belts, especially in Indonesia, which I would call a mining powerhouse. In this region, procurement focuses more on delivery speed and customization capabilities.
- North America & Europe: Stringent standards, with particular attention to international standards such as ISO, DIN, REACH, and RoHS. For example, the US has the strictest standards globally for flame-retardant conveyor belts used in underground mining. Product standards often dominate in this region.
- Africa, the Middle East, and South America: These regions are mostly mines and ports, involving long conveying distances and heavy loads. For example, the large gold mines in South Africa require wear-resistant, high-strength, and tear-resistant products, and rely more heavily on suppliers’ inventory and emergency response capabilities.
This is why large projects tend to choose established conveyor belt suppliers. They not only ensure you can “buy the product,” but also guarantee you can “get support at any time,” something many conveyor belt manufacturers currently lack.

1.4 Why are sometimes top suppliers more critical than ordinary manufacturers?
Leading suppliers don’t just “sell products,” they “shield risks from your path.”
They typically possess:
- More complete supply chain capabilities: inventory, delivery, shipping, and after-sales service.
- Stronger manufacturing integration capabilities: mass production + multi-standard systems (e.g., ST630–ST5400 steel cord conveyor belts). Factories may only have a greater advantage in producing a few products, but distributor-type conveyor belt suppliers often have more manufacturer resources, enabling them to supply almost all product categories.
- More stable compliance systems: for example, flame-retardant belts meeting GB/T 3685 testing requirements.
- Customization capabilities: heat-resistant conveyor belts compliant with GB/T 33510 standards.
- Project-level support: including emergency downtime solutions, splicing solutions, and maintenance recommendations.
- Global delivery experience: able to handle complex processes such as cross-border transportation, tariffs, documents of origin, and export compliance.

While manufacturers generally only control production, suppliers are the ones who truly help you manage risks.
Choosing top-tier conveyor belt suppliers isn’t because you lack a conveyor belt, but because you can’t afford the costs of project delays, equipment downtime, shipping delays, and invalid claims. Good suppliers can absorb these risks for you. This is one of the most crucial strategic choices in modern industry and a key foundation for the sustainable growth of your future business.
2. Conveyor Belt Suppliers and Key Application Industries: Who Really Impacts Global Industry Operations?
Each industry has different requirements for conveyor belts, and a good supplier’s ability to provide effective advice and products tailored to these differences determines whether your system operates continuously or experiences constant downtime.
To help you better determine which rubber conveyor belt suppliers are best suited for your business, I’ll guide you through the demand logic of major industries and why leading suppliers can truly become the “invisible foundation” of their respective sectors.
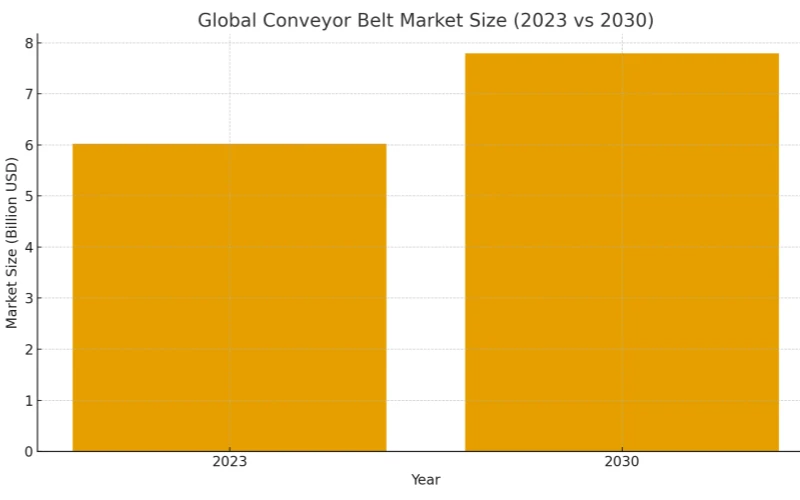
2.1 Global Market Size and CAGR Trend (Using the latest 2023–2030 data)
In recent years, the conveyor belt market has not been affected by global uncertainties; in fact, it has grown even faster. According to Maximize Market Research’s latest 2024 report, the global conveyor belt market reached approximately USD 6.02 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach approximately USD 7.79 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of approximately 3.74%.
Source :MMR
This growth is driven by clear structural forces:
- Fully automated e-commerce logistics systems are driving significant demand for light and medium-load conveyor belts.
- Recovering mining investment is increasing reliance on heavy-duty, long-distance, and wear-resistant conveyor belts.
- The eastward shift of manufacturing and supply chain restructuring are boosting overall demand for Asian suppliers.
- Upgrades in smart manufacturing are placing higher demands on the performance and stability of conveyor belts.
- Enhancing environmental regulations are driving companies to choose higher-quality, more durable products.
Therefore, regardless of your application industry, reliable conveyor belt suppliers are now “infrastructure providers” of industrial systems, not just product sellers.
2.2 Key Global Demand Regions and Growth Drivers: Why Suppliers Must Understand Regional Differences
Your market determines the type of supplier system you need, a point often overlooked by many buyers. Growth drivers vary significantly across regions, and excellent suppliers must be able to adapt to regional industry characteristics.
2.2.1 Asia Pacific (APAC)
- Global Manufacturing Base
- Rapid Expansion of Mining, Steel, and Cement Industries
- Intensive Engineering Projects, Common Large-Volume Orders
- Emphasis on “Price + Performance + Fast Delivery”
APAC’s reliance on rubber conveyor belt suppliers leans more towards “Capacity + Speed”.
2.2.2 North America and Europe
- Focus on Compliance (ISO, DIN, REACH, RoHS, CE)
- Stronger Requirements for Sustainable Production by Suppliers
- Emphasis on Modular, Intelligent Monitoring, and Energy-Saving Conveyor Belts
- Service, On-Site Response, and Technical Collaboration are More Important Than Just Price
Customers Here Truly Test a Supplier’s “System Maturity”.
2.2.3 Middle East, Africa, and South America
- Mostly Heavy-Duty Industries such as Mining, Metallurgy, and Energy
- Harsh Working Conditions, Extremely High Requirements for Wear Resistance, Heat Resistance, and Impact Resistance
- High Downtime Costs, Therefore, Strong Reliance on Suppliers’ Emergency Supply Capabilities
- Overseas Delivery and Inventory Support Determine Project Success
These Markets Test the Strength of Truly Capable Conveyor Belt Suppliers.
2.3 Global Supplier Industry Dynamics and Trends: Three Major Leap Forwards in the Supply Chain
I’ve personally witnessed the entire industry “upgrading” within the factory, with suppliers playing a more crucial role than ever before.
① Upgrades at the Production and Materials Level (Factory Capabilities → Supplier Capabilities)
Automated calendering, digital tension control, and intelligent vulcanization systems enable suppliers to provide more consistent products.
For example: Heat-resistant conveyor belts conforming to GB/T 33510 can withstand temperatures up to 200°C.
② Global Distribution Systems Are Becoming Faster (Inventory → Overseas Warehouses)
Leading suppliers are beginning to establish:
- Regional Warehouses
- Localized Inventory
- Transnational Shipping Collaboration Teams
This significantly improves system uptime.
③ Demand Shifts from “Standard Products” to “Specialty Solutions”
Especially in the mining, chemical, and metallurgical industries, the following features are being widely adopted:
- High-temperature resistance (passing GB/T 3512 heat aging test)
- Flame-retardant structure (complying with GB/T 3685 flame-retardant characteristic test)
- High-strength steel wire rope series ST630–ST5400
This is why top rubber conveyor belt suppliers can cover an increasing number of “irreplaceable working conditions.”
2.4 Key Application Industries: Why Does Every Industry Rely on Leading Suppliers?
Different working conditions require vastly different conveyor belts, and most industries no longer accept “general-purpose products.”
You must choose suppliers based on industry characteristics; otherwise, you are amplifying the risk.
2.4.1 Mining Industry: Heavy-Duty Operations Determine Only Strong Suppliers Can Handle the Tasks
- Long-Distance Continuous Operation
- High Impact, High Abrasion
- Large Material Particle Size, Harsh Environment
- Downtime = High Production Loss
Therefore, mines almost exclusively choose strong conveyor belt suppliers because they can provide:
- High-strength steel wire rope core series (e.g., ST1000–ST5400)
- Tear-resistant and impact-resistant structure
- Flame-retardant and high-temperature resistant formulations
- High-volume & rapid delivery capabilities
- Emergency solutions for line shutdowns
The stability of a mine depends on the supplier’s capabilities, not the manufacturer’s single process.

2.4.2 Logistics and Warehousing Industry: Speed, Reliability, and Low Noise are Key
Smart logistics centers and e-commerce warehouses have grown rapidly in the past five years, placing new demands on conveyor belts:
- High-Speed Operation
- Stable Surface Friction Coefficient
- Low Noise
- Modularization and Rapid Maintenance Capabilities
- Light-Load Abrasion Resistance
Here, the supplier’s inventory capacity + response speed are the hard indicators.

2.4.3 Food Processing Industry: Stricter Hygiene Requirements Than Any Other Industry
The food industry allows no room for error.
Your suppliers must understand:
- FDA/EC food-grade standards
- Oil-resistant, contamination-resistant, mildew-resistant, and antibacterial surfaces
- Easy-to-clean structure
- Complete material compliance documentation
Suppliers in this industry must understand both conveyor belts and regulatory documentation processes.

2.4.4 Construction and Packaging Industry: Consistency and Impact Resistance are Core Indicators
Common working conditions in the construction industry:
- Strong impacts from sand, gravel, cement, and aggregates
- Frequent start-ups and shutdowns
- High levels of environmental dust
The packaging industry emphasizes:
- High speed
- Stability
- Precise positioning
Both industries rely heavily on the product stability and rapid delivery capabilities of rubber conveyor belt suppliers.

2.4.5 Chemical Industry: Testing Suppliers’ Fundamental Material R&D Capabilities
Chemical operating conditions are complex and variable, requiring suppliers to possess genuine material formulation capabilities to provide:
- Acid and alkali resistance
- Corrosion resistance
- Oil resistance
- Aging resistance
- High temperature resistance (passing relevant tests in GB/T 33510 and GB/T 3512)
This industry’s requirement for suppliers is not “production capability,” but “R&D capability.”

Different industries have different operating logics, but they share one common point: Every industry cannot function without mature conveyor belt suppliers.
Suppliers who understand industry operating conditions and provide stable products and rapid delivery are becoming the core supporting force of the entire industrial system.
3. How to Evaluate True Top Conveyor Belt Suppliers? — Six Capabilities Determine Supplier Level, Not the Product Itself
In the conveyor belt industry, many mistakenly believe that “you can judge a supplier’s quality by looking at their product.” However, as you saw in the previous article, product capabilities belong to the Manufacturer, while system capabilities belong to the Supplier. Truly top-tier suppliers are not defined by “better products,” but by “more mature systems.” Buyers ultimately choose suppliers not based on parameters, but on whether they can “deliver the project safely.” Based on long-term experience in multinational collaborative projects, I have summarized six core criteria for evaluating suppliers. These six capabilities are not possessed by ordinary manufacturers, but only by mature supply chain-type suppliers.
3.1 Supply Chain Integration Capability: The ability to integrate resources is essential for handling complex orders
Manufacturers only possess their own production capacity, while suppliers can coordinate resources from multiple factories, with varying capacities and specifications, ensuring:
- Complex specifications can be integrated and completed in one go.
- Order structures can be flexibly split according to project schedules.
- Multi-specification mixed orders can be delivered simultaneously.
This means that buyers do not need to coordinate multiple manufacturers themselves, significantly reducing risk.
3.2 Delivery Capability: On-Time Delivery is More Important Than Performance
The biggest variable in cross-border procurement is not the product itself, but whether it can arrive on time. A true supplier must possess:
- Multi-route logistics solutions (sea, rail, inland transport)
- Shipping schedule coordination and container planning
- Delivery schedule stability and the ability to schedule production ahead of time
Buyers don’t want “speed,” they want “predictability.”
3.3 Operating Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capability: You provide the operating conditions, the supplier provides the solution
The reality is—80% of buyers only provide operating conditions, not technical parameters.
Top-tier suppliers must possess material judgment and structural matching capabilities, including:
- Belt structure judgment (EP/NN/ST)
- Abrasion resistance and temperature resistance rating of the cover adhesive
- The impact of the operating environment on adhesion, fatigue, and aging
- Providing cost reduction or lifespan extension solutions based on operating conditions
This capability is not possessed by ordinary manufacturers.
3.4 Project and Documentation System Capability: Multinational projects are most prone to bottlenecks in documentation, not the product itself.
Many buyers underestimate the importance of documentation. Engineering projects require:
- CO, COA, MSDS
- Third-party testing
- Certificate of Origin, Commodity Inspection, Bidding Authorization
- Parameter Tables, Risk Assessment, Structural Specifications
For medium to large-scale projects, 30-40% of the time is spent on “document review,” and only established suppliers can support this system.
3.5 Order Execution Capability: Only suppliers can ensure complex orders are error-free.
Orders for major projects often include:
- Multiple widths, multiple strengths, multiple batches
- Packaging, labeling, and pallets must be uniform for each batch
- Batch consistency must be absolute.
This is not a factory’s strength, but a supplier’s core capability.
3.6 Risk Management and Contingency Capability: Who do you contact when problems arise?
The true value of the supply chain is not when everything goes smoothly, but when problems occur:
- Urgent orders and order cancellations
- Mold changes
- Alternative solutions
- Transportation route changes
- Stock preparation support
- Third-party warehousing coordination
These situations are very common in multinational projects, and manufacturers often cannot provide rapid responses.

4. Top 10 Conveyor Belt Suppliers In the World
| Supplier Name | Official Web-Link |
|---|---|
| Tiantie Industrial Co., Ltd. | https://conveyorbeltchn.com |
| Continental Industry | https://www.continental.com/en/ |
| Bridgestone Industrial Products | https://www.bridgestone.com/ |
| Sempertrans (Semperit Group) | https://conveyor-belts.semperitgroup.com/ |
| Fenner Dunlop | https://fennerdunlopamericas.com/ |
| Gates Industrial | https://www.gates.com/ |
| ASGCO | https://www.asgco.com/ |
| Bando Chemical Industries | https://www.bandogrp.com/eng/ |
| Yokohama Rubber Conveyor Belt | https://www.y-yokohama.com/global/product/mb/conveyor-belts/ |
| Trelleborg Industrial Solutions | https://www.trelleborg.com/en/seals-and-profiles/products-and-solutions/conveyor-belts |
In this section, we will systematically introduce representative conveyor belt suppliers worldwide based on the six core supplier capabilities defined above—supply chain integration, delivery, operating condition matching and technology selection, project and documentation systems, order fulfillment, and risk management and contingency planning.
To ensure objectivity and industry neutrality, the list of companies presented in this section is not ranked in any particular order, nor is it sorted based on any single dimension. Each supplier has its own advantages and adaptability in different regions, operating conditions, and engineering scenarios. You can choose based on your project needs, location, budget, and the complexity of your operating conditions.
4.1 Tiantie Industrial Co., Ltd. (China)

① Supply Chain Integration Capability
As a typical “factory-type supplier,” Tiantie’s integration capability stems from its direct control over the production end. With its full-structure production lines (EP, NN, ST), it can integrate multiple widths, wear resistance grades, and strength grades within a single factory, significantly reducing communication costs for buyers in multi-SKU mixed orders. Simultaneously, its long-standing OEM service for regional brands in Asia, Africa, and South America allows for greater flexibility in specification conversion, batch unification, and alternative model selection, maintaining structural consistency in large orders or multi-batch projects. Compared to pure suppliers, its integration efficiency is higher; compared to single manufacturers, its SKU coverage is broader, suitable for engineering procurement with high specification complexity.
② Delivery Capability
Tiantie’s delivery system leans towards “flexible and adjustable,” with production scheduling adjusted based on shipping schedules, space availability, and project milestones, supporting rush orders or parallel production of multiple specifications. For concentrated maintenance periods, large-scale expansion projects, or annual framework orders, its delivery rhythm is stable and more flexible. Meanwhile, it maintains strong consistency in packaging, pallet labeling, and container loading schedules, ensuring smooth on-site integration across different batches. Compared to European and American suppliers, its delivery speed is faster; compared to regional distributors, its production capacity is more controllable, better meeting the time constraints of medium to large-scale projects.
③ Working Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Tiantie has extensive experience in high-temperature, heavy-load, and high-impact working conditions. It can comprehensively assess structures based on factors such as drop height, material temperature, humidity, abrasion rating, and roller diameter, rather than simply quoting prices based on EP/NN or abrasion resistance rating. It can mass-produce conveyor belts resistant to temperatures above 250°C, giving it stronger solution capabilities in high-temperature scenarios (such as sintering lines, lime kilns, and foundries). In the mining industry, it has a clear structural matching logic for the combined loads formed by impact rating, material particle size, and drop height, and can provide reasonable thickness and layer designs based on risk points, reducing the risk of incorrect structural selection for buyers.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
Tiantie offers a comprehensive export and engineering documentation system, including COA, CO, third-party testing, raw material compliance declarations, temperature/abrasion resistance test results, and GB/T and ISO series tests. Packaged documents commonly required by project-based clients (bid documents, parameter tables, compliance declarations, production batch instructions) can also be formatted to better suit the document review habits of local governments or EPCs. While its documentation system leans towards an engineering style, it is comprehensive and accurate, suitable for international engineering projects requiring rigorous review.
⑤ Order Execution Capabilities
In mixed orders (different widths, abrasion resistance grades, and strength grades), Tiantie maintains batch consistency and standardized packaging. Particularly in large-volume orders, it maintains stable management of roll weight, roll length, pallets, and labels, reducing the workload of unpacking and verification on-site. Its execution end is highly adaptable to changes, additional quantities, and early delivery, and can adjust the pace according to the project site conditions, which meets the real needs of “dynamic scheduling” in multinational engineering projects.
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Capabilities
Tiantie’s risk management mechanism is primarily reflected in its production scheduling flexibility and alternative structure reserves. In the event of raw material fluctuations, equipment maintenance, or temporary shutdowns, orders can be transferred to other production lines through internal coordination, or technically feasible contingency structure solutions can be provided to ensure that critical engineering lines are not delayed due to production scheduling or raw material factors. For cross-border customers, the most critical contingency capability lies in “being able to find the right person and handle the situation immediately.” Tiantie’s long-term supply experience in the OEM market gives it practical responsiveness in emergency production intervention, rapid document generation, and quick rescheduling.
4.2 Continental Industry (Germany)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
Continental’s supply chain system is top-tier in the industry, with integration capabilities spanning multiple production bases, regional warehousing systems, and a complete distribution and technical service network. Conti can unify production lines in Europe, America, and Asia into a single planning system, ensuring high consistency across multiple factories, specifications, and projects within the supplier system. Its industrial product line is comprehensive, especially in high-standard mining, energy, and underground engineering fields, where it can simultaneously integrate different grades of flame-retardant, heat-resistant, low-elongation, and wire rope series. For multi-regional projects (such as multinational mining groups), Continental can provide a cross-regional supply system with a unified structure, quality, and documentation—an advantage that is difficult for ordinary factories to achieve.
② Delivery Capabilities
Conti’s delivery system relies on its global warehousing network and predictive scheduling system. For regions such as Europe and North America, relatively controllable inventory delivery can be achieved. Meanwhile, for mining and energy customers, there are periodic framework agreements to reduce delivery uncertainty. While its production schedule is stricter and its ability to handle urgent orders is not as strong as that of Asian suppliers, its delivery accuracy is extremely high. Transportation documents, customs clearance materials, packaging standards, and batch control are all highly standardized, which is beneficial for executing major projects or government-level engineering needs. Compared to flexibility, its advantage lies in “stability and predictability.”
③ Operating Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Continental has a strong data-driven foundation in operating condition analysis. Its selection system leans towards standardization, formulaic approaches, and failure model analysis. Whether it’s high-drop ore, underground coal mine flame retardancy, long-distance main transport lines, or extreme abrasion environments, Conti recommends structures primarily through its internal database, material life models, and customer usage records. Its unique advantage in intelligent monitoring and energy-saving structures makes it suitable for customers with extremely high requirements for “lifecycle cost (LCC).” The disadvantage is that it has lower flexibility for atypical operating conditions or projects with limited budgets.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
Conti’s documentation system is considered an industry benchmark, extremely detailed, compliant, and systematic, meeting the high standards of review by the EU, North America, mining groups, and energy groups. Whether it’s REACH, RoHS, flame retardant reports, abrasion resistance ratings, ISO series testing, or third-party inspections and batch traceability, its document formats are complete and standardized, making it ideal for bidding, government approvals, and multinational EPC projects. For projects requiring rigorous document review, Conti is the most reliable choice.
⑤ Order Execution Capabilities
Continental’s order execution system is highly digitalized, with internal production planning centrally scheduled. While it doesn’t support highly flexible multi-change order insertions, it excels in standardized orders, annual framework supply, phased delivery, and project phased progress coordination. Its packaging, labeling, palletizing, and batch tracking are strictly standardized, reducing the risk of batch confusion in large projects.
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Capabilities
Strong risk management capabilities are mainly reflected in its compliance system, production stability, and cross-plant backup capabilities. Despite its more rigorous production system and limited room for adjustment, Conti can reduce supply uncertainty through multiple factory backups, regional inventory, and a multinational service network. For the mining, power, and energy industries, Conti’s greatest value lies in its near-zero error reliability, rather than its rapid response.
4.3 Bridgestone Industrial (Japan)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
Bridgestone’s supply chain integration capabilities are renowned for their high consistency. Its production system, distributed across Japan and Thailand, is regionally concentrated yet deeply unified, enabling high SKU consistency, minimal performance fluctuations, and extremely low batch variations in heavy-duty and mining sectors. For clients requiring consistent standards across different mining areas (e.g., multinational mining companies, or a main production line with multiple branch lines), Bridgestone can provide a long-term, stable structural combination, which is its core value as a supplier. Its integration capabilities are stronger than those of mid-sized suppliers in Japan and Southeast Asia, but slightly less comprehensive than European integrated suppliers in terms of product range.
② Delivery Capabilities
Bridgestone’s delivery system leans towards stability over speed. Due to its rigorous production scheduling and highly standardized production processes, Bridgestone boasts a high delivery accuracy rate, but it is less adaptable to urgent orders and significant changes. For “critical mainline” projects in mining areas or heavy industry, this delivery style is actually considered an advantage because of its extremely low supply volatility. However, if projects require extremely short lead times or frequent adjustments, Bridgestone is not the most flexible option. In Japan and parts of Southeast Asia, its regional inventory and service system allows for rapid response.
③ Working Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Bridgestone has a strong advantage in structural selection for high-impact, high-drop, and heavy-load mines, with its wire rope structures and fatigue resistance being industry-leading. Its selection style tends to be conservative, favoring maximizing safety under risk conditions, while demonstrating high accuracy in judging key indicators such as impact load, drum diameter, and material particle size. If the buyer seeks a “critical structure” with a lower budget, Bridgestone typically does not offer overly compressed options, making it more suitable for “failure-intolerant” mainline projects.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
Bridgestone has a complete documentation system, but its style is traditional; the format is clear, but the visualization level is not as high as that of European suppliers. Reports on flame retardancy, abrasion resistance, tensile properties, and wire bonding strength required for common projects are readily available and highly reliable. For projects with stringent government reviews or third-party testing processes, the data is highly credible, but the format flexibility is relatively low.
⑤ Order Execution Capability
Bridgestone’s order execution stability is excellent, with extremely low change and error rates, a key reason for its long-term adoption by mines. Consistency in multi-batch, multi-stage deliveries is very high, especially in batch control of the main wire rope line and key conveyor belts, where errors are virtually nonexistent. The drawback is its limited adaptability to temporary customer demands.
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Capability
Bridgestone’s risk management follows a “reliability-first model.” Its contingency capability does not rely on flexible scheduling but rather on the fundamental principle of “extremely low product failure rate.” This risk model is highly effective for main mining lines that must guarantee continuous operation for many years. However, its response speed is slower than supply chain systems in China or Southeast Asia when faced with sudden additional orders or emergency order insertions.
4.4 Sempertrans (Austria)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
Sempertrans’s integration capabilities primarily stem from its two major production bases in Europe and India, covering regions such as Europe, Central Asia, and the Middle East. They excel at providing “quasi-standardized combinations” for mid-to-high-end applications, including EP, heat-resistant, flame-retardant, and abrasion-resistant series, which are highly suitable for projects requiring EU compliance and high batch consistency. Their product range is broader than Bridgestone’s, but not as extensive as the former two in the ultra-heavy-duty wire rope series. Sempertrans’s integration capabilities lean more towards product category depth than SKU breadth.
② Delivery Capabilities
Sempertrans’s delivery schedule is stable, but production cycles are long and inflexible. Delivery accuracy is high for European projects, but for intercontinental clients (Africa, South America, Middle East), transportation and production scheduling can affect overall delivery speed, resulting in slower overall delivery. The advantage is complete compliance documentation and easy project approval; the disadvantage is that it is not suitable for urgent orders or clients with very large annual consumption volumes.
③ Operating Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Sempertrans’s selection style leans towards “high durability + medium-to-high safety factor,” offering significant advantages in high-temperature, abrasion-resistant, and continuous operation conditions (such as cement, steel, and metallurgy). Flame-retardant and heat-resistant series meet high EU standards, suitable for engineering projects with stringent regulations. For extreme heavy-duty applications (such as hard rock mines and ultra-long main lines), its style is robust, but its performance ceiling is not as high as Bridgestone or Yokohama.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
Sempertrans’s documentation system highly conforms to European standards; its standardized, aesthetically pleasing, and formatted documents are a significant advantage. COA, REACH, RoHS, third-party testing, and flame retardant/abrasion-resistant grade documents are all precisely formatted, making them easily usable in EPC and government tenders. In regions with stringent project reviews and high document thresholds (Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa), its compliance is highly valued.
⑤ Order Execution Capabilities
The execution system is rigorous, but with limited room for adjustment. In practice, this translates to: slow execution, but stable execution. For multi-batch orders or long-cycle supply plans, its consistency is excellent, but its adaptability to changes, additional demands, and urgent deliveries is weak. It is suitable for engineering clients with “clear project schedules and well-developed upfront planning.”
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Capabilities
Due to its rigid production scheduling system, Sempertrans’ contingency capabilities are limited. However, its risk management is characterized by “extremely low quality fluctuations + high factory stability,” reducing after-sales risks. In regions with high regulatory requirements, compliance systems and traceability systems are its biggest risk control measures, rather than rapid response capabilities.
4.5 Fenner Dunlop Americas (USA)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
Fenner Dunlop’s integration capabilities are primarily reflected in its “heavy-duty mining and coal mine flame-retardant systems.” Its two major production systems in the US and Australia are highly unified, capable of integrating medium- and heavy-duty products such as the MSHA flame-retardant series, high-impact steel wire rope series, and high-strength fabric series. For coal and hard rock mines in North America and Australia, its SKU portfolio is broad and highly consistent. Globally, Fenner’s integration capabilities are concentrated in the mining sector rather than covering multiple industries; therefore, its adaptability to specific working conditions is better than its cross-industry integration capabilities.
② Delivery Capabilities
Fenner’s local delivery speed in Europe, America, and Australia is relatively fast, relying on regional inventory and localized production. However, intercontinental transportation (such as to South America, the Middle East, and Asia) is significantly affected by flight distances and production schedules, resulting in longer delivery cycles. As a supplier to major mining clients, Fenner’s delivery system prioritizes accuracy over speed. Major mines typically replenish their stock through annual or quarterly orders, enabling them to maintain stable supply without relying on flexible production scheduling.
③ Operating Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Fenner’s selection capabilities are most prominent in scenarios involving extreme impact, high tear risk, and high drop. Its wire rope and high-tear fabric structures are frequently used in critical mainlines in North American and Australian mines. Its MSHA flame retardant system is one of its globally unique strengths, suitable for underground coal mines with stringent regulatory definitions. For light industry or food processing, Fenner’s operating condition matching breadth is less than that of European and Japanese suppliers, but its judgment on mining operating conditions is extremely accurate, and its risk assessment is mature.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
Fenner’s underground mining flame retardant documentation complies with the most stringent MSHA standards, giving it a significant advantage in North American mining projects. Its documentation system is technically oriented, including numerous extended testing items (tear, impact, joint strength, etc.). While its documentation meets international engineering requirements, its formatting and visualization levels are slightly lower than those of European suppliers. For projects primarily focused on compliance (such as government mining permits), Fenner is an extremely stable choice.
⑤ Order Fulfillment Capability
Fenner has a mature order fulfillment system, particularly adept at managing a “periodic replenishment + multiple large orders” model. Fenner maintains high stability in meeting mine requirements for dimensional consistency, coil weight consistency, and pallet standardization. Its weakness lies in its limited adaptability to ad-hoc demands and emergency changes, but for the routine operations of the mining industry, Fenner’s execution style is considered safe and reliable.
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Planning
Its contingency planning capabilities are built on “high localization + low failure rate.” In core regions like the US and Australia, it can provide alternative models and expedite delivery through regional inventory. However, in intercontinental markets, its contingency planning capabilities are less advantageous. Fenner’s risk control model is similar to Bridgestone: reducing the occurrence of risks rather than dealing with emergencies after they occur.
4.6 Gates Industrial (USA)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
Gates possesses significant “multi-industry SKU coverage capabilities” in supply chain integration. It can integrate light-duty, industrial, manufacturing logistics, and some medium-duty rubber conveyor belt products. It also boasts a large-scale distributor network, giving it strong SKU combination capabilities for small-to-medium batch, multi-batch, and multi-scenario orders. While not known for heavy-duty mining products, its cross-industry integration breadth far surpasses many specialized suppliers, making it more suitable for consolidated procurement of multiple models and materials in manufacturing, packaging, logistics, e-commerce, and other industries.
② Delivery Capabilities
One of Gates’ biggest advantages is its “rapid delivery system.” Thanks to its global distribution network and regional warehousing system in over 100 countries, small-to-medium batch orders can be responded to quickly. Its OEM and distribution models allow for some inventory in most regions, enabling buyers to obtain faster delivery speeds than direct factory supply. The disadvantage is that if the demand is for heavy-duty, high-strength, or customized products, Gates’ delivery speed will decrease significantly.
③ Working Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Gates excels in selecting materials for light and medium load conditions, accurately assessing friction coefficients, tension matching, and turning radius requirements for industries such as manufacturing, agricultural machinery logistics, packaging, and e-commerce warehousing. However, in mining, metallurgy, high-temperature, and high-impact environments, its structural limitations are less than those of Continental, Bridgestone, or Fenner, thus limiting its application to general industrial environments. While its technology selection range is broad, its depth in the heavy-duty sector is limited.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
Gates boasts a comprehensive and standardized documentation system, providing ISO, RoHS, safety declarations, bills of materials, parameter files, and other standardized documents in a clear and easy-to-read format. This documentation is highly user-friendly for clients requiring tender documents, government reviews, and project assessments. However, its heavy-duty product line is relatively limited, resulting in less in-depth documentation compared to other heavy-duty brands for projects requiring large quantities of wire rope or high-temperature, flame-retardant heavy-duty series.
⑤ Order Execution Capabilities
Gates’ streamlined order execution system is well-suited for supply models involving multiple SKUs and frequent replenishment. It excels in executing small-batch and multi-batch orders with high efficiency and adaptability, enabling rapid collaboration with regional clients (such as Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Europe). However, it is not the most adept supplier for large-scale, heavy-duty, and mining-related annual orders.
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Capabilities
Thanks to its distribution and inventory systems, Gates possesses strong contingency capabilities for “regular and small-to-medium specifications,” enabling rapid replenishment, model replacement, and emergency shipment arrangements. For large-scale projects or customized products, its contingency capabilities are limited. Overall, Gates is more suitable as a comprehensive supplier offering “stable backup + rapid response,” rather than a supplier for extreme operating conditions.
4.7 ASGCO (USA)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
ASGCO’s integration focus is not on the conveyor belt itself, but on the “entire conveyor system ecosystem.” It can integrate idlers, cleaners, redirection devices, structural components, and belt supplies to form complete system solutions. Therefore, its system integration capabilities surpass those of most traditional conveyor belt suppliers. However, its conveyor belts rely on partner factories for manufacturing, making its heavy-duty product portfolio less comprehensive than that of full-system manufacturers. It is suitable for customers requiring “system integration, rather than single-product procurement.”
② Delivery Capability
ASGCO has strong delivery capabilities in North America, relying on regional inventory and localized technical teams. It has a complete range of system components and a large inventory of standard parts, resulting in fast equipment delivery. Conveyor belt delivery depends on the production scheduling and allocation of partner factories. In intercontinental markets (such as Asia, the Middle East, and Africa), its delivery time is significantly longer than in Europe and America, therefore its strongest competitive advantage remains concentrated in North America.
③ Working Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capability
ASGCO’s working condition assessment is more “systematic,” excelling at analyzing on-site issues such as belt misalignment, spillage, accumulation, and impact zones. However, its ability to match the working conditions of the conveyor belt itself depends on the product portfolio of its partner factories and is not as strong as top brands like Continental and Bridgestone. Therefore, it is very strong in “system optimization” and moderately strong in “belt structure assessment,” suitable for customers who want suppliers to assume some engineering responsibilities.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
ASGCO’s documentation system leans more towards equipment and systems, including installation guides, component matching lists, on-site rectification plans, and cleaning system adjustment parameters. For conveyor belts, its documentation relies on partner factories, resulting in significant format differences. For North American mining clients, its documentation system is sufficient for review; for multinational EPC projects, the completeness of its documentation depends on the partner factory.
⑤ Order Execution Capabilities
ASGCO possesses extremely strong execution capabilities for conveyor system equipment (such as idlers and cleaners), with short production cycles, clear specifications, and ample inventory. However, for conveyor belt orders, its execution capabilities are constrained by partner factories, with batch consistency and change response speeds lagging behind suppliers with their own production systems. It is suitable for mixed procurement of “equipment + conveyor belts” rather than large-scale centralized procurement.
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Capabilities
ASGCO’s contingency capabilities are primarily focused on the system equipment end, rather than the conveyor belt end. For emergency supply disruptions or order cancellations of conveyor belts, their response speed is affected by the partner factories; however, for system problems (such as poor cleaning, belt misalignment, and material spillage), their on-site technical team can quickly provide solutions. Therefore, the value of their risk management lies in “maintaining system stability” rather than resolving conveyor belt supply chain risks.
4.8 Bando Chemical (Japan)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
Bando’s supply chain integration capabilities are primarily reflected in its “light-duty and medium-duty conveyor belt systems” and “cross-industry SKU adaptability.” It boasts a rich product line in manufacturing, logistics equipment, packaging machinery, and agricultural transmission, enabling it to integrate various products such as light-duty conveyor belts, industrial belts, and synchronous belts into a single project supply list, making it a common choice for customers with “multi-category, small-batch, and high-frequency procurement.” The drawback is its limited integration capabilities in steel wire rope, high-temperature heavy-duty, and mining SKUs, thus its overall coverage remains biased towards the light industry and equipment sector.
② Delivery Capabilities
Bando’s delivery schedule is very stable, especially for standard specifications and light-duty products. Leveraging its regionalized production system across Asia and its comprehensive dealer network, it achieves rapid response. For customized conveyor belts or large-volume cross-regional orders, the delivery time is longer than that of typical OEM factories, but the stability is higher. Its supply model has been proven over time and is suitable for the “planned replenishment” rhythm of the manufacturing industry, but not for the “temporary rush orders + large-volume emergency replacement” conditions in mining.
③ Working Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Bando’s selection advantages lie in precision manufacturing, packaging, logistics, automated conveying, and agricultural machinery, accurately judging indicators such as flexibility, turning force, oil resistance, and low noise. It excels in “light-duty professionalism” compared to most Asian suppliers. The disadvantage is that its structural upper limit is not suitable for heavy-duty scenarios such as high drops, ore impacts, large particles, and 200°C high temperatures; therefore, its technology selection leans more towards industrial automation than heavy industry.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
Its documentation system is comprehensive and standardized in format (common style in Japanese manufacturing), including material safety declarations, oil resistance ratings, coefficients of friction, and service life data. However, in industries requiring heavy-duty, high-temperature, and flame-retardant conveyor belts, its documentation depth is inferior to European brands (lacking the depth of MSHA, DIN 22109, and GB/T 3685 series). Therefore, it is more suitable for factory equipment procurement than for high-intensity bidding processes in mining, metallurgy, or large-scale EPC projects.
⑤ Order Execution Capability
Bando excels in orders with “multiple SKUs, high-frequency replenishment, and small batches,” demonstrating fast execution and a low error rate. For companies requiring frequent replacement of small-specification conveyor belts (such as food packaging plants, furniture manufacturers, and logistics warehousing lines), its order execution capability far surpasses that of large-scale heavy-duty rubber manufacturers. Its shortcomings include: unsuitability for large mining orders with mixed specifications; and a lack of production line capabilities for executing ultra-wide, ultra-thick, and ultra-high-strength orders.
⑥ Risk Management and Emergency Response Capabilities
Bando’s emergency response advantage lies primarily in its “standard parts inventory + regionalized distribution system.” Regular light-duty products can be quickly replaced, allowing for rapid repair of production line failures. However, it lacks substantial emergency response capabilities for heavy-duty conveyor belts or large-scale sudden incidents. Therefore, it is generally suitable for the stable operations of light industry, automation, and equipment manufacturing companies, rather than the high-impact scenarios of heavy industry.
4.9 Yokohama Rubber (Japan)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
Yokohama focuses on medium- and heavy-duty rubber conveyor belt systems. Its integration capabilities are concentrated on engineering-grade products such as EP, NN, steel wire rope (ST series), and wear-resistant and heat-resistant conveyor belts. Its SKU portfolio is more focused on mining, ports, and heavy industry than Bando, making it one of the few Japanese brands with “full-structure medium- and heavy-duty” capabilities. Its light-duty product coverage is limited, therefore its integration capabilities emphasize “engineering depth” rather than “industry breadth.”
② Delivery Capabilities
Yokohama’s delivery model is known for its “stable cycle”—not the fastest, but extremely stable, suitable for annual framework orders and critical main operating lines. Delivery is relatively fast for the Southeast Asian and Japanese domestic markets, but large-volume orders for the Middle East, Africa, and South America will have longer lead times due to production cycles and long supply chains. Overall, it is suitable for engineering clients with “predictable production schedules,” rather than users with urgent orders.
③ Working Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Yokohama’s biggest advantage lies in “materials science + heavy-duty structural design.” Its wire rope products excel in fatigue strength, tear resistance, and adhesion, making them suitable for high-drop, high-impact, long-distance, and heavy-duty working conditions (such as large open-pit mines and iron ore ports). In terms of heat resistance, its products are more stable than most Asian suppliers, but the upper temperature limit is not as high as Tiantie’s 250°C+ series. Overall, its selection capabilities lean towards heavy-duty and engineering-grade applications, with weaker coverage in the light-duty field.
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
The documentation system is rigorous but leans towards a traditional Japanese style (engineering-oriented, clear diagrams, less text). It can provide ISO, JIS, adhesion testing, heat resistance testing, fatigue testing, and other documentation required for engineering projects, suitable for technical reviews of large ports, mines, steel mills, and energy projects. However, its drawbacks include: less visualization capabilities compared to European counterparts; and some EPC clients in certain regions requesting more “internationally formatted” documents.
⑤ Order Fulfillment Capability
Yokohama boasts high order fulfillment accuracy for “critical heavy-duty single-line applications” (e.g., ST2000–ST5400), with excellent batch consistency, making it suitable for annual procurement in medium to large-scale mining projects. However, its execution flexibility is not as good as Asian suppliers, with a slower response time to structural changes, additional orders, and rapid replenishment. It is more suitable for projects with “stable demand” rather than “dynamic demand”.
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Capability
Due to its stable production rhythm and extremely high requirements for structural consistency, Yokohama’s risk control model is “avoiding risk occurrence.” For sudden demand, its contingency capability is not as good as suppliers like Tiantie or Gates, but its products themselves have an extremely low failure rate, making it a “safe brand” for critical heavy-duty lines. For high-risk industries (mining, ports, energy), this low failure rate is itself part of risk management.
4.10 Trelleborg Industrial (Sweden)

① Supply Chain Integration Capabilities
Trelleborg’s core integration focuses on “special material systems,” particularly chemically resistant, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for extreme temperature environments, as well as insulating rubber products. While its conveyor belt coverage is not as extensive as Yokohama or Conti, it has a unique advantage in “special purpose SKUs.” Its supply chain integration capabilities lean towards “depth” rather than “comprehensiveness,” making it suitable for demanding procurement in chemical, metallurgical, and highly corrosive environments.
② Delivery Capabilities
Trelleborg delivers quickly in Europe, moderately in North America, and longer in Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East. Its overall production scheduling leans towards “customized production,” making it unsuitable for rush orders. Its delivery system emphasizes material consistency and quality priority rather than speed, making it more suitable for demanding special operating conditions than large-scale routine projects.
③ Operating Condition Matching and Technology Selection Capabilities
Trelleborg possesses world-leading material technology in areas such as chemical media, highly corrosive environments, and high-temperature furnace conveying—especially excelling in chemical resistance, oil resistance, acid and alkali resistance, and high-temperature buffering capabilities. However, its capabilities are less advanced than heavy-duty brands (such as Bridgestone or Fenner) for mining, port, or heavy-duty applications. Trelleborg’s selection capabilities are characterized by “professional depth” rather than “industry breadth.”
④ Project and Documentation System Capabilities
As a European brand, its documentation system is detailed and its ESG information is transparent, including chemical material declarations, VOC emission data, and chemical resistance test data. This makes it suitable for projects requiring rigorous document review, such as those in chemical plants, smelters, and pharmaceutical factories. The drawback is that in mining and logistics projects, the documentation may be overly specialized and not fully match the engineering document requirements.
⑤ Order Execution Capabilities
Trelleborg’s order execution core lies in “high consistency and high professionalism.” Its batch and material consistency are excellent, but its flexibility is insufficient. For large-volume, multi-specification orders, its execution speed is not as fast as that of comprehensive suppliers, making it suitable for large-scale, special-condition projects using a single model.
⑥ Risk Management and Contingency Capabilities
Trelleborg products are typically used in “failure-prone” conditions, therefore its risk management focuses on the materials and their stability, rather than supply chain contingency. Thus, its contingency capabilities are moderate, but the probability of product failure is extremely low, making it a high-safety choice in special environments such as chemical corrosion, high temperatures, and hazardous materials transportation.
5. Why does the mining industry truly need top-tier Conveyor Belt Suppliers, not just manufacturers?
5.1 Why must the mining industry rely on a “supplier system”? It’s not just about a roll of rubber belt.
If you’ve ever worked in a mine, you know that purchasing conveyor belts is never about “buying a product,” but about “buying security.” Mines operate at full capacity daily in high-impact, high-dust, and high-abrasion environments. If the main line stops, the losses can accumulate in hours.
This is where the value of suppliers is amplified.
Manufacturers can make products, but suppliers can provide “continuous supply + end-to-end support.”
Mining conditions amplify all risks, therefore, mines need:
- Stable delivery
- Rapid response
- Compliance documentation
- Technology selection
- Large-scale coordination
- Emergency stock
- Engineering communication
These are the biggest differences between conveyor belt suppliers and manufacturers.

5.2 Why is Tiantie’s dual role as “supplier + manufacturer” more suitable for mines?
I must tell you directly: mines fear “uncertainty” the most.
Simply being able to produce conveyor belts isn’t enough—you also need to ensure:
- Customers can reach you
- Projects can find you
- You can solve ad-hoc problems
- You can keep up with the pace during major overhaul seasons
- You can handle annual frame procurement
This is Tiantie’s core advantage over ordinary manufacturers:
① Capable of both production and supply chain problem-solving
Ordinary factories only handle production, while Tiantie can handle:
- Production scheduling coordination
- Multi-specification parallel supply
- Annual inventory strategy
- On-site parameter matching
- Real-time order structure adjustment based on projects
This capability is typically found only by suppliers, but Tiantie also possesses bargaining power on the production side.
② Dual-line experience of OEM + Own Brand
Do you know why Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America are willing to entrust their local brands to Tiantie for OEM manufacturing?
It’s not because it’s cheap, but because:
“He can provide the full supply chain capabilities that brands need, which ordinary factories can’t.”
③ Factory-level customization capabilities + supplier-level delivery flexibility
Other suppliers only “coordinate supply,”
other factories only “produce products,”
but Tiantie is “I can both make and deliver.”
This is the stability that mines want most.

5.3 In mining projects, what problems can suppliers solve for clients that manufacturers can’t?
This is the most valuable part of your article, and what readers truly care about.
① Enables one-time coordination of multiple specifications, strengths, and large quantities
Commonly used in mining:
- Extremely long distances
- Different widths
Different strengths (EP/NN/ST) Ordinary manufacturers require production scheduling cycles, but suppliers can coordinate resources to complete projects in one go.
② Project-level delivery (not product-level delivery)
Only suppliers can provide:
- Transportation coordination
- Shipping schedules
- Export documents
- Inspection agreements
- Dimensional and parameter documents
- Regional compliance documents (e.g., MSHA, GB, EN)
Many factories are not good at this area.
③ Emergency response capabilities (most valued by mines)
The greatest value of a supplier lies here:
“You can find someone.”
This is more important than any performance aspect in overseas projects.
5.4 Why do mining customers prefer to establish long-term partnerships with “supplier-type factories”?
The partnership between mines and conveyor belt suppliers isn’t a one-off transaction, but rather a long-term relationship that can last 3-5 years, or even 10 years.
What they value is:
- Guaranteed annual supply;
- Availability for timely replenishment;
- Guaranteed stable quality;
- Long-term, repeat supply;
- Providing technical documentation;
- Helping them reduce uncertainty.
This is the true value of top-tier rubber conveyor belt suppliers.
You’re not just selling belts; you’re selling:
- Stability;
- Delivery;
- Safety;
- Continuous supply;
- Risk hedging;
- Project success rate.
And these are precisely Tiantie’s most outstanding advantages—being both a manufacturer capable of producing high-performance conveyor belts and a supplier capable of supporting large-scale projects.
This is an ecological strength that ordinary factories can never achieve.

6. Performance and Strategies of Leading Suppliers in Core Import Markets
6.1 North American Market: High Automation, High Standards, and Emphasis on Supply Chain Stability
North America is one of the regions globally with the most stringent requirements for industrial conveyor belts. The procurement logic here is very clear: Safety, Compliance, and Sustainability > Price.
Especially in industries such as logistics automation, open-pit mining, and e-commerce warehousing, there is a clear preference for conveyor belts with:
- MSHA flame retardant standards
- High-strength frame
- Long-term continuous operation capability.
North American customers tend to partner with conveyor belt suppliers with a long track record because of high local labor costs, significant downtime losses, and greater sensitivity to delivery reliability and after-sales response. European and American brands maintain a strong presence here, while Asian suppliers with OEM/factory advantages are continuously increasing their market share through more flexible delivery and economies of scale.
6.2 European Market: High Quality + High Environmental Standards Dominate Purchasing Decisions
Europe is the most mature and “standards-intensive” conveyor belt market globally.
The characteristics here are quite clear:
- Strict EU environmental regulations (REACH, RoHS)
- High quality system requirements
- Customers place greater emphasis on sustainability and ESG performance
The European market has stricter requirements for the material safety, volatile organic compound (VOC) control, heat resistance, and flame retardancy of rubber conveyor belts. Therefore, brands such as Continental, Sempertrans, and Phoenix have long held a dominant position in Europe.
At the same time, European customers place greater emphasis on total cost of ownership (TCO), that is, “how long the product can last and whether it can operate stably,” which raises the industry barriers for leading rubber conveyor belt suppliers in the region.
6.3 Asia-Pacific Market: High Demand, High Growth Rate, Intensive Engineering Projects
The Asia-Pacific region is the fastest-growing market globally, including China, India, and Southeast Asia.
Driven by:
- Infrastructure construction
- Manufacturing expansion
- Heavy industry growth
- Demand from open-pit mining and building materials industries
The characteristics of this region are: large order sizes, diverse operating conditions, and fast delivery.
Therefore, suppliers who truly gain market share in the Asia-Pacific region typically possess the following characteristics:
- Large-volume production capacity
- Flexible production scheduling
- Customization capabilities
- Cost controllability
Manufacturers like Tiantie and Double Arrow have a clear advantage here, while global brands are also responding to this market through localized production and more flexible supply strategies.
6.4 Middle East, Africa, and South America: Resource-Driven, Strong Demand for Wear-Resistant and Heat-Resistant Products
These three regions share a common characteristic: a “resource-based economy,” including mines, ports, cement plants, and the energy industry.
In these regions, the three most important capabilities for conveyor belts are:
wear resistance, heat resistance, and tear resistance.
The challenges in these regions are also significant:
- Harsh environment
- Long transportation distances
- Uncontrollable project cycles
- High logistics costs
- Prone to rush orders
Therefore, customers are more concerned about suppliers’:
- Long-distance supply capabilities
- Engineering-grade product stability
- Export and logistics experience
- Multi-specification mixed order supply capabilities
Asian suppliers with manufacturing advantages are growing rapidly in these regions, while European and American brands maintain their position in high-end mining and special working conditions.
6.5 Lessons from Regional Differences for Buyers: Strategies Must Be Tailored to Local Conditions
Different regions have vastly different needs for conveyor belts, which is the core reason why global conveyor belt suppliers must allocate resources according to region.
For buyers, this means:
- North America: Prioritize compliance and safety levels.
- Europe:Focus on environmental protection and total lifecycle costs.
- Asia Pacific:Focus on scale, customization capabilities, and delivery time.
- Middle East/Africa/South America: Prioritize companies with strong wear resistance, heat resistance, and stable supply capabilities.
In other words, no single company can dominate all markets,
but leading suppliers will establish core barriers to entry in key regions.
7. Market Challenges and Opportunities: Structural Changes Facing Global Conveyor Belt Suppliers
7.1 Raw Material Price Volatility: Supply Chain Stability Becomes a Core Competitive Advantage
Key materials such as natural rubber, carbon black, steel wire rope, and reinforcing fabric continue to experience cyclical fluctuations, and these fluctuations are more frequent than before. Natural rubber and steel wire rope raw materials, in particular, play important roles in international futures markets.
These changes bring challenges beyond just cost, including:
- Shorter price validity periods
- More difficult supply chain forecasting
- Increased inventory management pressure
- More flexible production scheduling is needed
Leading conveyor belt suppliers, due to their stronger coordination and forecasting capabilities, can actually establish a stronger stability advantage in this context. Strong conveyor belt suppliers have dedicated professional procurement and finance teams that assess the international market and make large-scale purchases at appropriate times, often ensuring the best product quality at the lowest cost.

7.2 Global Competition Shifts from “Price Competition” to “Delivery, Supply Chain, and Stability Competition”
In the past, the industry primarily focused on “low-price competition.” Even today, some buyers in certain countries and some low-end brands still seek suppliers with the lowest prices. However, the major trend has shifted:
- Who can deliver faster?
- Whose supply chain is more stable?
- Whose export and logistics system is more mature?
- Who can handle project-based orders?
Due to increased logistical risks and shorter project cycles, suppliers relying solely on low prices have less room to survive, while suppliers with complete supply chain capabilities are becoming the long-term choice for customers.
7.3 Decreasing Costs of High-Performance Materials: Structural Opportunities for Suppliers to Plan Ahead
High-strength fibers, heat-resistant formulations, and lightweight skeletons were previously used primarily in extreme working conditions due to their high cost. However, as supply chains mature and costs gradually decrease, the following demands are expanding to more industries:
- High-drop conveying
- Medium- and high-temperature operating conditions
- High-impact ore
- Long-distance main transport lines
The opportunity for suppliers here is: Not only to provide materials, but also to guide customers in assessing lifespan, budgets, and construction conditions, helping them make the “long-term cost-optimal” choice.
7.4 High Demand and High Uncertainty from Emerging Market Expansion
Southeast Asia, South America, Africa, and the Middle East continue to experience growth. The demand for conveyor belts in these regions has two characteristics:
- Rapid growth and concentrated demand
- High environmental uncertainty (transportation, customs clearance, policies, road conditions, warehousing, etc.)
To establish a foothold in these regions, suppliers need stronger:
- Export experience
- Localization understanding
- Document and customs clearance capabilities
- Flexible shipping and consolidation mechanisms
- Large-volume coordination capabilities
These regions often test supply chain capabilities more directly than the product itself.
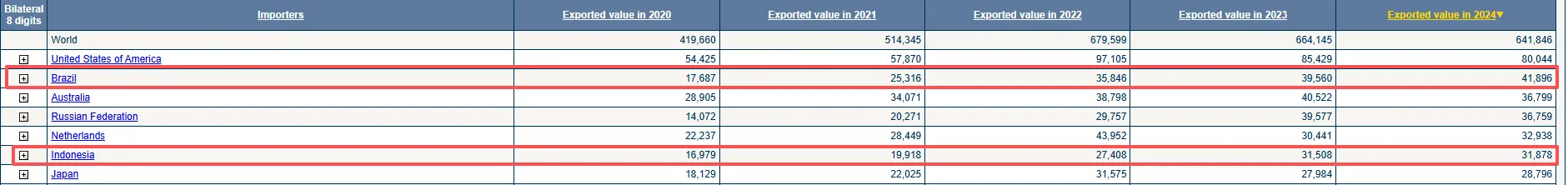
7.5 ESG and Increased Global Compliance Requirements: Suppliers Are No Longer Just “Intermediaries”
As global sourcing places greater emphasis on traceability, the role of suppliers within the ESG framework is changing. Large projects increasingly require:
- Raw material sourcing documentation
- Environmental impact statements
- Production process data
- Material safety statements
- More transparent supply chain records
Suppliers must be able to retrieve, organize, integrate, and present this information from the manufacturing end to customers.
Those who can provide complete compliance documentation will have an advantage in the procurement systems of large EPC projects, state-owned enterprise projects, and multinational corporations.
7.6 Increased Logistical Uncertainty: Delivery Capacity Becomes a Key Competitive Advantage
Changes in global shipping costs, port congestion, and regional policy shifts are continuously impacting delivery cycle costs.
For industries reliant on continuous production (such as mining, cement, steel, and ports), delivery uncertainty is more critical than product materials.
Therefore, a supplier’s core strength is no longer solely reflected in their products, but also in:
- Shipping schedule coordination capabilities
- Multi-channel logistics solutions
- Transportation risk control
- On-site delivery planning
- Long-distance transportation packaging capabilities
“Stable delivery” is becoming the core standard for customers evaluating suppliers.
7.7 Increased Project-Based Demand: Suppliers Must Possess Comprehensive Engineering Collaboration Capabilities
Large-scale projects such as mines, steel mills, and cement plants commonly adopt the Project Integration (EPC/EPCM) model.
This means the supplier’s role has upgraded from “selling equipment” to:
- Coordinating with project timelines
- Cooperating with third-party testing
- Providing technical documentation
- Providing customs clearance documents
- Adjusting specifications according to project requirements
- Coordinating multiple shipments
- Participating in annual supply guarantee plans, also known as annual orders
The better a supplier can adapt to the “project rhythm,” the more likely they are to become a long-term partner for the client.
7.8 The Market is Converging Towards a “Large Supplier Ecosystem”: Increasing Pressure on Small and Medium-Sized Players
As supply chains become more complex, customers are increasingly favoring:
Large suppliers that can:
- Bear risks
- Provide stable inventory
- Coordinate across regions
- Have emergency response capabilities
- Ensure continuous supply
While smaller suppliers are flexible, they struggle to meet the following project requirements:
- Large volume
- Multi-specification mixed orders
- Stable production scheduling
- Documentation and compliance
- Long-term framework contracts
- Technical documentation support
The industry is concentrating on the strength of its suppliers.
7.9 The More Complex the Market Environment, the More the Value of Leading Conveyor Belt Suppliers is Highlighted
From raw materials to logistics, from compliance to projects, from emerging markets to material updates, the complexity of the conveyor belt industry is continuously increasing.
This is not an obstacle for suppliers, but rather a crucial stage in accelerating industry stratification.
Suppliers capable of:
- Stable delivery
- Stable supply
- Stable quality
- Stable documentation
- Stable communication
will naturally gain higher customer loyalty.
For the purchasing party, this means: Choosing a supplier = choosing stability, predictability, and risk control capabilities,
which will directly affect the project success rate and overall TCO.

8. Industry Trends Driving Supply Chain Logic Restructuring: The Future of Conveyor Belt Supply Models
8.1 The Number of Market Suppliers is Increasing, but the Proportion of Suppliers Capable of Consistent and Stable Delivery is Declining
While the number of global conveyor belt suppliers continues to expand, the proportion of suppliers capable of maintaining high stability over the long term is shrinking under stricter quality requirements, compliance processes, and engineering scenarios.
Reasons include:
- Increased requirements for quality consistency
- Greater differences in operating conditions
- More complex documentation systems and testing requirements
- More refined cross-border delivery chains
- Clearer boundaries of after-sales responsibility
This has led to a structural change in the industry: “More supply choices, but stratified stable supply capabilities.”
8.2 Cross-border delivery methods are constantly evolving, settlement cycles are gradually lengthening, and credit requirements for the supply chain are increasing.
Compared to ten years ago, export transactions have shifted from primarily EXW and FOB models to a deeper credit system:
- 30–90 days L/C
- L/C at sight → L/C after installation
- Some orders are settled only after six months to a year of use.
This shift in settlement methods implies higher quality traceability and stricter division of delivery responsibilities.
The supply side must possess stronger delivery stability and a closed-loop quality system to meet the credit requirements of cross-border projects.
8.3 The increasing proportion of project-based procurement makes original equipment manufacturer (OEM) authorization and documentation systems crucial.
More and more global projects are adopting centralized bidding models, significantly increasing the participation of material suppliers in the project process.
A typical change is that large-scale projects, government projects, or group projects require suppliers to directly issue authorization documents, and even participate in local bidding under the supplier’s name.
This reflects the industry’s increased reliance on “original manufacturer endorsement” and indicates that suppliers are playing a further upstream role in the supply chain of large projects, moving beyond traditional supply nodes.
8.4 Widening Differences in Operating Conditions Make Material Selection More Reliant on Supplier’s Structural Judgment Capabilities
As industries such as mining, ports, cement, and power evolve towards more specialized and complex operating conditions, conveyor belt selection is no longer simply a matter of EP/NN, strength grade, or cover rubber thickness.
End-users more commonly rely on suppliers to make professional judgments on structural combinations after providing information such as material characteristics, temperature, drop, and abrasion environment.
This trend increases the technical density of suppliers during the selection phase and deepens their technical responsibility within the engineering system.
8.5 Material Supply is Trending Towards Integration, with Suppliers Taking on More Integration Roles for Non-Core Materials
An increasing number of engineering projects tend to have core suppliers handle the integration of materials for the entire conveyor system, including non-core products such as idlers, drive rollers, and cleaners.
This is not because suppliers possess full production capacity, but rather because the industry tends to reduce collaboration nodes to lower communication costs, improve system compatibility, and shorten supply chain cycles.
Conveyor belt suppliers are increasingly assuming the role of material integrators in many scenarios, even if some products are not their core business.
8.6 The extended cycles of raw material and logistics fluctuations make the supply chain more reliant on stable pricing systems and cost forecasting capabilities.
Price fluctuations in core materials such as rubber, carbon black, and steel wire rope are becoming shorter and more significant, and global transportation costs remain persistently unstable.
In this context, the supply system needs to possess:
- Annual price range planning
- Alternative material solutions
- Transparent cost structures
- Matching service life with budget models
Stability and predictability are becoming key indicators in future supply models.
8.7 Compliance systems have become a rigid requirement for global projects; document completeness impacts supply chain continuity.
Global engineering projects are increasingly demanding compliance, including:
- COA
- MSDS
- Third-party testing
- Flame retardant, heat-resistant, and abrasion-resistant standard reports
- ISO and CE standards
- Original manufacturer authorization
- Original origin and material traceability
Supply chains must possess robust document control systems and compliance management capabilities to continuously participate in the procurement phase of large-scale projects.

8.8 Increased technical responsibility of material suppliers in regions lacking engineering support
In some regions, due to a lack of local engineering personnel, material selection, structural assessment, risk warnings, and system compatibility analysis are often undertaken by the supply chain.
In these markets, the supply side plays the role of “extended engineering capabilities,” rather than simply a product supplier.
This trend will further intensify as projects become more specialized.
8.9 Supply system stability, technology density, and documentation maturity will become key stratification points in the future industry.
In summary, industry changes over the next five years will exhibit several distinct trends:
- Increased supply choices, but more pronounced stratification in stable supply capabilities.
- Increased project-based procurement, leading to greater reliance on original equipment manufacturer (OEM) authorization and documentation systems.
- Wideer-widening differences in operating conditions make structural selection more dependent on supplier expertise.
- Upgraded payment and settlement methods require suppliers to assume deeper credit responsibilities.
- Increased demand for integrated supply chains places suppliers in a more proactive role within the system.
Structurally, the role of suppliers is evolving from “delivery provider” to “system collaborator.”
Technology selection, documentation systems, supply stability, and material integration capabilities will determine the core position of suppliers in the future supply chain.

9. How Supply Chains Ensure Efficiency and Reliability in Complex Operating Conditions and Cross-Border Logistics
9.1 A Stable Delivery System is the Foundation for Continuous Project Operation
In cross-border material supply chains, any single point of delay can cause project shutdowns.
Therefore, mature supply chains typically ensure delivery stability through the following methods:
- Collaborative production scheduling across multiple factories or production lines
- Prepared inventory of key specifications
- Multiple shipping/land transport route planning options
- Order splitting strategies to reduce concentration risk
- Maintaining long-term and stable partnerships with logistics service providers
- Establishing dedicated delivery timelines for large-scale projects
These mechanisms enable the supply chain to maintain strong resilience in the face of regional policy changes, freight rate fluctuations, or port congestion, thereby ensuring that project materials arrive within a predictable timeframe.
9.2 Standardized Documentation Systems Improve Customs Clearance Efficiency and Project Compliance
From the perspective of international engineering execution, a complete documentation system is not only related to compliance reviews but also directly affects customs clearance speed and the efficiency of large-scale project approvals.
A mature supply chain typically includes:
- Standardized documentation such as COA, MSDS, Certificate of Origin, and third-party inspection records
- A traceable production batch management system
- Flame retardant/heat resistance/mechanical performance testing tailored to project requirements
- Factory authorization and standardized bidding document templates
- ISO/CE compliant technical documentation structure
These standardized documentation systems significantly reduce customs clearance delays, bid rejections, or audit failures caused by incomplete documentation, contributing to overall project schedule control.
9.3 Technical Selection Capability Determines System Stability and Service Life
The stability of a conveyor belt system highly depends on the accuracy of its selection, including:
- Fabric structure
- Strength grade
- Abrasion layer thickness
- Skeleton material
- Temperature/oil resistance/flame retardant rating
- Joint processing method
As operating conditions become increasingly diverse, technical judgment requires comprehensive analysis of factors such as material density, drop, impact coefficient, humidity, temperature, and environmental abrasion.
Supply chains capable of providing stable structural selections are more likely to maintain lower failure rates and more controllable maintenance cycles over long-term operation.
9.4 Supply Chain Coordination Enhances Execution Efficiency for Large-Volume Orders
In large projects, large-scale changeovers, or centralized cross-regional material distribution, supply chain coordination capabilities determine execution efficiency.
Core capabilities include:
- Timeline control for multiple shipments
- Batch consistency management
- Synchronization of shipping schedules and production plans
- Integrated material packaging (conveyor belts + idlers + rollers, etc.)
- Matching arrival times with EPC or construction units
This collaborative mechanism enables the supply system to maintain accuracy in time and quantity within complex engineering environments, reducing rework and waiting time.
9.5 Quality Consistency Mechanism Ensures Long-Term System Reliability
Stable operation depends not only on the material’s inherent performance but also on consistent quality control within the factory, including:
- Raw material stability and traceability system
- Parameter consistency during cooling, vulcanization, and molding stages
- Cover rubber ratio and hardness control
- Fabric layer alignment and adhesion strength inspection
- Pre-shipment sampling and full inspection mechanisms
- Complete laboratory testing capabilities (tensile, abrasion, peel strength, etc.)
Higher quality consistency reduces the probability of deviations during field use and makes maintenance cycles more controllable.
9.6 Integrated Supply System Reduces Collaboration Costs and Technical Compatibility Risks
In an increasing number of engineering scenarios, the materials in conveying systems include not only the conveyor belt itself but also components such as idlers, rollers, tensioners, and anti-deviation devices.
The advantages of an integrated supply system are:
- Higher system compatibility
- Easier parameter matching
- More unified transportation and customs clearance schedules
- Material arrival sequence can be organized according to system logic
- Clearer after-sales and warranty responsibilities
Through material integration, the difficulty of engineering execution can be significantly reduced, resulting in higher overall efficiency.
9.7 Enhanced Engineering Support Capabilities Improve Controllability in Complex Operating Conditions
In regions lacking engineering resources or with incomplete system information, the technical support capabilities of the supply chain are particularly crucial, including:
- Operating Condition Analysis
- Structural Recommendations
- Explanation of Specification Differences
- Lifespan Estimation
- Risk Warnings (Impact from Drop, Temperature Range, Humidity, Material Particle Size, etc.)
A supply chain with engineering support capabilities can reduce frequent maintenance issues caused by incompatibility, improving overall system stability.
9.8 Reliable Delivery and Standardized Technical Support Reduce Long-Term Operating Costs
In summary, the advantages of a mature supply chain include:
- Stable Engineering Delivery
- Complete Compliance Documentation
- Accurate Technical Judgment
- Strong Supply Chain Resilience
- High Integration of System Components
- Clear After-Sales Response
These capabilities not only affect project schedule but also long-term operating costs, maintenance frequency, and total cost of ownership (TCO).
A stable supply chain provides more controllable operational assurance throughout the project lifecycle.
9.9 Systematic Supply Capabilities Are Becoming a Key Selection Criterion for Future Engineering Projects
As the complexity of working conditions, the difficulty of cross-border delivery, and the scale of project-based procurement continue to increase, the supply model is shifting from “product supply” to “systematic delivery capabilities.”
Capabilities including delivery, technology, compliance, coordination, and material integration will become the main tiers of the future supply system and a key factor in the successful implementation of engineering projects.

10. Key Parameters to Confirm in Procurement and Cooperation
10.1 Core Parameter System for Conveyor Belt Supply Quotations
In cross-border material supply chains, the specifications of conveyor belts not only determine the unit price but also directly affect system lifespan, delivery time, material compatibility, and subsequent maintenance frequency. A complete parameter system typically includes the following:
● Material Type
The particle size, density, moisture content, temperature, and impact coefficient of different materials affect the fabric layer structure, cover rubber type, and abrasion resistance grade. For example, ores, clinker, coal, sand, and grain all have different abrasion characteristics and working environment requirements.
● Belt Strength Grade (EP/NN/ST Series)
EP and NN are suitable for different flexibility requirements, while the ST series with steel cord cores is often used for long-distance, large-drop, and heavy-load conditions. The choice of strength grade determines the system’s safety factor and load-bearing capacity.
● Number of Fabric Layers and Longitudinal and Transverse Tensile Strength
The number of fabric layers affects the overall impact resistance and tear resistance. The selection of fabric layer structure under different operating conditions typically requires evaluation in conjunction with drop, material density, and idler roller design.
● Abrasion Resistance Grade
The abrasion resistance of the cover rubber directly determines its lifespan. High-abrasion conditions usually require higher-grade abrasion-resistant rubber compounds to reduce the frequency of later maintenance and replacement.
● Oil, Chemical, and Corrosion Resistance Systems
Chemical, metallurgical, and waste treatment scenarios have strict requirements for rubber compound formulations; improper selection can lead to premature aging and structural failure.
● Temperature Resistance Grade (up to 250°C and above)
High-temperature conveyor belts need to have stable hot air aging performance (e.g., according to test methods such as GB/T 3512). In operating conditions of 180–250°C, the cover rubber formulation and skeleton stability are particularly critical.
● Environmental Conditions (Humidity, Dust, Acidity/Alkalinity, etc.)
Special environments can affect bond strength, surface properties, and service life. For example, high-humidity and high-salinity environments often require additional anti-corrosion treatment or structural optimization.
● Order Size and Delivery Cycle
Large-volume projects typically require phased delivery, involving production scheduling coordination, long-cycle pre-production, and multi-batch inspection systems. Delivery schedule and order size need to be confirmed simultaneously.
These parameters collectively form the foundation for conveyor belt selection and pricing, and are also key elements for the safety and stability of the engineering system.
10.2 Differences in Supply Models and Choice of Cooperation Logic
As engineering projects expand, the supply system is showing clear stratification. The differences between different cooperation methods are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
● Manufacturer Direct Supply Model
The manufacturing end has advantages in product structure, material, and quality consistency, but is usually limited in:
- Multi-specification integration
- Cross-regional coordination
- Document system
- Stock preparation capacity
- Delivery flexibility is limited.
● Supplier System (including OEM, project-based supply chain, and multi-factory collaboration)
Suppliers have greater adaptability in supply chain flexibility, compliance documentation, project coordination capabilities, and multi-SKU integration. Capable of handling:
- Long-term framework planning
- Multi-batch delivery
- System material integration
- Large-scale project document support
- Work condition structure recommendationand other more complex cooperation requirements.
● Channel inventory model
Suitable for short lead times, standard specifications, and rapid replacement scenarios. However, its capabilities are limited in non-standard specifications, multi-layered work conditions, and multi-batch projects.
● Engineering service and solution ecosystem model
In large-scale EPC, mining, cement, and port projects, the supply system is not just a delivery node, but an integral part of project schedule management, including:
- Material arrival rhythm control
- Work condition analysis and structural matching
- Contact with construction parties
- Synchronization of test reports
- Quality consistency assurance
In such scenarios, a systematic supplier has a clear advantage.
10.3 Pre-cooperation parameter and system confirmation helps reduce project execution risks
Clearly defining the corresponding parameter system, work condition, document requirements, and delivery nodes before project initiation can significantly reduce uncertainties in subsequent project execution.
Mature supply chains typically ensure cooperation stability through the following mechanisms:
- Standardized technical documents and specification confirmation forms
- Sample and batch consistency verification
- Operating condition risk assessment
- Delivery milestone schedule development
- Synchronization of multiple batch plans
- Third-party inspection coordination
- Pre-production capacity and scheduling planning
- Alternative material solutions prepared
These mechanisms collectively form the underlying framework of a stable supply system, which is particularly crucial in cross-regional projects, high-temperature operating conditions, high-altitude transport, or long-term operation systems.

11. Frequently Asked Questions
11.1 Why is the scope of the supply chain typically broader than that of the manufacturer?
In global engineering scenarios, the supply chain often handles multi-factory collaboration, cross-regional inventory integration, document management, compliance support, project coordination, and multi-SKU integration.
The manufacturing end focuses more on production, while the supply chain needs to handle:
- Coordinating multiple batch shipments
- Integrating different specifications
- Original manufacturer authorization system
- Multi-country testing requirements
- Project on-site progress management
Therefore, the supply chain covers a longer chain and participates in stages closer to the core nodes of project execution.
11.2 How does the quality evaluation system affect uptime and total cost of ownership (TCO)?
The quality of the conveyor belt is determined not only by the materials but also by:
- Stability of the cover rubber formulation
- Layer adhesion
- Molding uniformity
- Consistency of the heat vulcanization process
- Joint quality
- Batch consistency
A high-quality system can significantly reduce unplanned downtime and extend maintenance intervals, making the total life cycle cost (TCO) of the system more controllable.
Conversely, an unstable quality system increases maintenance frequency and spare parts consumption, creating greater uncertainty for continuous operation.
11.3 Can high-temperature resistant conveyor belts withstand operating conditions above 200°C for extended periods?
The performance of high-temperature resistant conveyor belts is determined by the rubber compound formulation, the reinforcing material, and thermal aging stability.
According to thermal aging standards such as GB/T 3512, high-quality heat-resistant conveyor belts maintain stable adhesive strength and cover rubber performance within the long-term 180–200°C range.
Under specific formulations, some systems can withstand short-term material temperatures above 250°C.
The key is not the “temperature resistance number,” but whether the residual strength after hot air aging meets long-term operational requirements.
11.4 Will new materials (such as Kevlar/aramid) completely replace traditional plywood structures?
New materials possess high strength, lightweight, and excellent heat resistance, but are more expensive and require more stringent processing conditions.
New materials have significant advantages in long-distance, extreme high-temperature, or high-impact applications. However, in most routine operating conditions, EP/NN still maintains a comprehensive advantage in terms of cost and performance.
As material costs decrease, the penetration rate of new materials may increase, but they will not completely replace traditional structures in the short term.
11.5 How to assess the delivery capacity and emergency response capability of a supply chain?
Supply chain capability is typically assessed from the following dimensions:
- Production cycle stability
- Scheduling flexibility
- Multi-factory collaboration capability
- Key specification inventory reserves
- Multiple transportation route options
- Document completeness (reducing customs clearance delays)
- Control of the rhythm of multiple shipments
In emergency situations, a supply chain that can schedule production immediately, coordinate logistics in advance, and quickly provide alternative specifications has a greater advantage.
11.6 Why are global distribution networks and B2B response speed important metrics for a supply chain?
With shorter project cycles and increased cross-border trade, response speed directly affects material arrival time and project progress.
A supply system with a mature distribution network typically possesses:
- Shorter inquiry response time
- More standardized document processes
- Multi-regional inventory preparation and feedback mechanisms
- Stronger multi-language and multi-timezone support capabilities
These capabilities significantly reduce communication costs and schedule risks in projects.
11.7 Why do some engineering projects require suppliers to directly participate in bidding or provide authorization?
With the increasing standardization of global engineering projects, more and more bidding parties require:
- Original manufacturer authorization
- Original manufacturer’s name in the bidding
- Third-party testing reports
- Original manufacturer’s compliance documents
- Complete technical parameter certification
Supplier participation makes the entire bidding process more reliable and transparent, avoiding systemic risks caused by information asymmetry or inappropriate structural selection.
11.8 Why does “only the working conditions are provided, and the supplier is responsible for specification selection” often occur in engineering procurement?
In many end-use scenarios, engineering teams do not possess professional capabilities in materials and structures.
Therefore, in common operating conditions, it is more common to provide:
- Material characteristics
- Impact from drops
- Conveying length
- Temperature range
- Ambient humidity and dust conditions
Structural assessment (number of fabric layers, strength grade, type of cover adhesive) is completed by the supplier to ensure that the selection achieves a balance between engineering requirements and material performance.
11.9 Under what circumstances is integrated supply necessary, rather than separate procurement of conveyor belts?
In scenarios with high system integrity requirements (mines, cement plants, ports, etc.), conveyor belts typically work in conjunction with components such as idlers, drive rollers, and tensioning devices.
If supplied by multiple suppliers, the following may occur:
- Inconsistent specifications
- Different arrival times
- Additional transportation and customs clearance costs
- Difficulty in defining after-sales responsibility
- Increased errors in connection links
Therefore, more and more projects tend to have the key supply system handle overall material integration to reduce project execution uncertainty.
11.10 Is technical support from the supply system suitable for all engineering projects?
The necessity of technical support depends on the complexity of the project itself.
Under normal operating conditions, basic specifications are sufficient.
However, in the following scenarios, technical support has a significant impact on system stability:
- High-temperature materials
- Multi-point drop
- High humidity or high salinity environments
- Long-distance transportation
- Extremely high wear scenarios
- Government or large group bidding projects
- Scenarios requiring third-party review
In these situations, the structural assessment, risk prediction, and documentation provided by the supplier can significantly reduce system operational risks.


















