1. What is EP in Conveyor Belt
1.1 Definition and Basic Characteristics of EP
Many new customers will ask: “What is EP in EP conveyor belt?” The “EP” in EP conveyor belts refers to polyester-nylon, which refers to two different materials used in the core layer of the conveyor belt. Specifically, EP conveyor belts are composed of two high-strength synthetic fibers, polyester and nylon. After reasonable arrangement, they have excellent tensile strength, impact resistance and tear resistance. Polyester fibers are usually used in the longitudinal direction to enhance the longitudinal tensile performance of the belt body; nylon fibers are used in the transverse direction to improve the impact resistance and tear resistance of the belt body. This arrangement structure makes it particularly good when handling heavy loads and long-term conveying tasks.
1.2 Role of EP in Conveyor Belts
So, why are EP conveyor belts so important? First of all, the combination of polyester and nylon fibers gives the EP belt extremely high durability and strength, allowing it to function in long-term, high-load working environments. Its core advantage is that it can ensure that the conveyor belt can still operate stably under most harsh conditions.
- Tensile Strength:The polyester layer of the EP conveyor belt provides very strong tensile strength, while the nylon layer enhances impact resistance. Even in the case of heavy objects falling or mechanical shock, the EP conveyor belt can still effectively withstand and reduce damage.
- Low Elongation:During use, the EP conveyor belt will not be over-stretched or relaxed like some other materials. It maintains stable tension and ensures the long-term operation of the conveyor belt.
- Wide Adaptability: Whether in high temperature, low temperature, or humid environment, the EP conveyor belt can perform stably and is widely used in mining, construction, logistics and other industries.
For every occasion that requires long-term, heavy-load conveying tasks, EP conveyor belts are the best choice. Especially for industrial applications that require a long time to run and have high impact resistance requirements, EP conveyor belts can provide you with strong protection.
2. Composition of EP Conveyor Belts
2.1 Components of EP Conveyor Belts
EP conveyor belts are composed of three main components: Top Cover, core layer and Bottom Cover. Each layer is designed with its specific function, which together determine the performance and application range of the conveyor belt.
Top Cover
The top cover is the upper surface of the conveyor belt, which is used to directly contact the transported materials. It needs to protect the inner layer from wear, chemical corrosion or temperature changes. According to application requirements, the top cover layer can adopt different rubber tensile strength standards to enhance wear resistance, oil resistance, anti-static properties and other properties, so the top cover is generally thicker.
Core layer
The core layer is the core part of the EP conveyor belt, usually woven from synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon, providing the strength and tensile resistance of the conveyor belt. The thickness and density of the core layer are crucial to the load capacity and durability of the conveyor belt. At the same time, it also affects the bending performance and fatigue resistance of the conveyor belt, including multiple core layers such as steel cord.
Bottom Cover
The bottom cover mainly plays a role of protection and reinforcement. It needs to resist the wear of the back of the conveyor belt and the contact with the roller, but because the bottom cover does not need to directly contact the material, the bottom cover is generally thinner than the top cover .
These three layers work together to ensure the efficient operation of the EP conveyor belt under various working conditions and meet the needs of different industries.
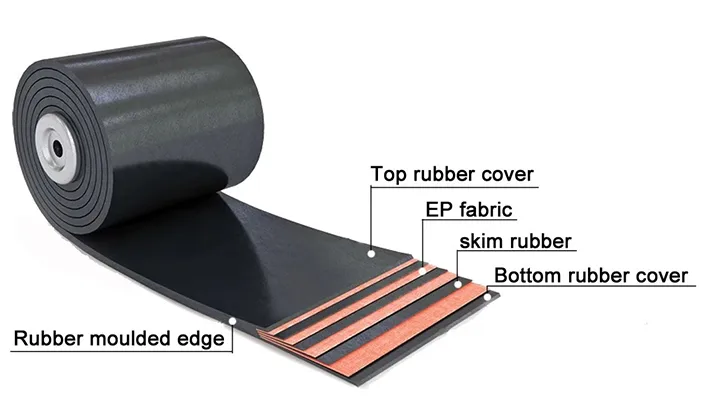
2.2 Structure of reinforcement and base materials
The core layer of the EP conveyor belt can be divided into the reinforcement layer and the base material layer. The structure is usually an interlaced layer, that is, polyester and nylon fibers are interlaced in a specific direction to form a mesh structure. This structure not only enhances the strength of the conveyor belt, but also provides additional flexibility to ensure that it can cope with various complex working environments during operation.
- Reinforcement layer: As the “protective shield” of the conveyor belt, the reinforcement layer is usually woven from nylon fibers to enhance its impact resistance and tear resistance. When the conveyor belt is subjected to external pressure, the reinforcement layer can effectively buffer and disperse the pressure and protect the base material layer.
- Base material layer:The polyester fibers in the base material layer are tightly combined during weaving, which enhances the tensile strength and stability. It can maintain a stable state under high load and high speed operation conditions, reducing elongation and deformation.
This combination of composite materials ensures that EP conveyor belts can provide longer service life and higher stability even under harsh conditions.
2.3 Function and material of the top cover layer
The top cover of the EP conveyor belt directly contacts the conveyed material and provides protection during the conveying process. The main functions of the top cover are:
- Protection:The top cover can protect the internal substrate layer from the wear of the material and the invasion of the external environment, especially when transporting sharp or heavy objects, to avoid direct damage to the conveyor belt.
- Chemical resistance:Depending on the use environment of the conveyor belt, the top cover usually uses different materials and materials of different standards. For example, the surface chemical resistance of the conveyor belt for transporting strong acids and alkalis is stronger than that of the conveyor belt for transporting coarse salt.
- Heat and Cold resistance: The material of the cover layer will also be adjusted as needed to adapt to a specific temperature range. For example, some special covers can withstand temperatures up to 200°C, that is, heat resistant conveyor belts, while others have better low temperature adaptability, cold resistant conveyor belts.

2.4 Other Auxiliary Materials and Processes
In addition to the basic core layer and cover layer, the manufacturing process of EP conveyor belts may also involve some auxiliary materials and processes, such as:
- Antistatic treatment:In environments where static electricity accumulation needs to be prevented, such as mines, EP conveyor belts can be added with 3%-5% antistatic agent to ensure safe operation.
- Anti-UV materials:For conveyor belts exposed to sunlight, anti-UV additives can extend their service life and prevent ultraviolet rays from aging the material.
- Oil resistance treatment:Some EP conveyor belts will enhance their oil resistance through special processes, which are suitable for industries such as petrochemicals and food processing.
The use of these auxiliary materials and processes enables EP conveyor belts to work stably in more diverse environments, increasing their application range.
3. Advantages of EP Over Steel Cord Conveyor Belt
When choosing conveyor belts, some buyers and engineers will hesitate between EP conveyor belts and steel wire core conveyor belts. While both offer great support and durability, they’re different enough to make a choice. Let me take you through some of the significant advantages of EP conveyor belts compared to steel cord conveyor belts.
A simple understanding of steel cord conveyor belt is to replace the ep core layer with a steel wire rope core. At this time, what is related to the strength is the thickness and thinness of the diameter of the single steel wire in the steel wire rope core, not the number of layers.
3.1 Strength and Durability
Although EP conveyor belts cannot compete with steel cord conveyor belts in terms of strength, they are more durable and adaptable. Steel cord conveyor belts are made of multiple steel wires twisted into multiple steel cords as the core. They are suitable for very high-strength working environments and perform particularly well in heavy-load applications.
But if you are concerned about long-term operating stability, the wear resistance and tear resistance of EP conveyor belts are enough to cope with various environments. Its structure is formed from a combination of polyester and nylon, a design that allows it to perform particularly well under light to medium loads.
For example, if you need a conveyor belt to handle general material transportation without having to deal with extreme weights such as giant ores with sharp edges, EP conveyor belts are definitely an economical and durable choice. Although steel wire rope cores are dominant in high-strength applications, for most mining and construction sites, the high efficiency and low maintenance costs of EP belts are undoubtedly attractive highlights.

3.2 Cost-Effectiveness
When it comes to cost, EP conveyor belts are undoubtedly the more advantageous choice. Steel cord conveyor belts are usually more expensive due to their high strength and complex manufacturing process, as well as the material of the steel cord cores they use. EP conveyor belts use simpler manufacturing processes and materials, which can greatly reduce costs. In many industries, especially medium-duty applications, EP conveyor belts provide the same or even better performance while saving money.
For example, in industries such as sand and gravel transportation, food and agriculture, EP conveyor belts can provide sufficient durability, and the price is much lower than that of steel wire core conveyor belts, which means that you can achieve stable operation for a longer period of time with less investment. , avoiding the trouble of frequent replacement and maintenance.
3.3 Flexibility and Ease of Installation
Another advantage of EP conveyor belts is their enhanced flexibility. Compared with steel cord conveyor belts, EP belts are lighter and easier to install. Although the structure of the steel wire rope core is strong, it often requires more roller support due to its strong rigidity. EP conveyor belts can adapt to more complex paths and bends, making installation and maintenance easier.
For example, in some working spaces that are narrow or have excessively undulating terrain, EP conveyor belts can adapt to larger height differences and more complex operating environments, reducing trouble during the installation process. This flexibility makes it preferred in many scenarios.

3.4 Maintenance and Lifespan
Another benefit of EP conveyor belts is lower maintenance requirements. Because it is not as susceptible to metal fatigue or breakage as steel cord conveyor belts, it requires less frequent maintenance over long-term use. Even under frequent operation, the EP belt can maintain good condition, avoiding frequent replacement of parts or high-cost repairs.
Especially in non-high load environments, EP conveyor belts can provide long-lasting service. Although the steel wire rope core belt can handle extremely high loads, due to its metal core layer and the environment in which it is used, it is easily damaged and requires more professional maintenance.
3.5 Environmental and Sustainability Benefits
Finally, we have to mention the performance of EP conveyor belts in terms of environmental protection and sustainability. Because it uses common synthetic materials such as polyester and nylon, and less metal materials are involved in the production process, the environmental impact during production and disposal is relatively low. Compared with steel cord conveyor belts, EP conveyor belts are more in line with modern environmental protection standards.
With the increasing awareness of environmental protection, many industries are more inclined to choose low-carbon, recyclable materials, which also gives EP conveyor belts obvious advantages in environmental protection.

4. Representation Method of EP Conveyor Belt
When we discuss EP conveyor belts, it is important to understand how to represent and interpret their specifications. This not only helps us make wise choices when purchasing, but also ensures that we get the conveyor belt that best suits our needs. Next, I will take you through the specification numbers of EP conveyor belts to help you clearly understand what these symbols mean.
4.1 Explanation of Specification Numbers
The specification number of EP conveyor belts usually includes several key elements, and each number or letter has its own unique meaning. For example, the detailed EP specification number format is usually “EP500 1200MM 4P 5+2 200M DIN-Y“, in which each part represents different characteristics. Let’s analyze them one by one:
- EP:This is the core logo of the conveyor belt, indicating that it uses a hybrid structure of polyester and nylon as reinforcement materials.
- 500:This is the strength grade of the conveyor belt, usually in N/mm. This number indicates the maximum tensile force that the conveyor belt can withstand per millimeter of width. In this example, “500” means that each millimeter of belt width can withstand a tensile force of 500 Newtons.
- 1200MM:This refers to the width of the conveyor belt. In this example, “1200MM” means that the width of this belt is 1200mm.
- 4P:This refers to the number of layers of the core layer of the conveyor belt. Here “4P” means that this belt has 4 plys
- 5+2:This number represents the thickness of the cover layer, usually the thickness of the top and bottom cover layers. In this example, “5+2” means that the top cover is 5 mm and the bottom cover is 2 mm.
- 200M:This refers to the length of each roll of the conveyor belt. Here it is expressed as “200 meters” for each roll of the conveyor belt.
- DIN-Y:The specification of the cover rubber. The “-” is generally the abbreviation of different standards in different countries. The letters after the “-” generally refer to the type of cover rubber. Different letters represent different tensile strength, elongation, abrasion, and hardness. Here DIN-Y means German standard, Y type cover rubber, tensile strength ≥ 20MPA, elongation ≥ 400%, abrasion ≤ 150mm³, hardness 60±5 Shore.

After understanding these specifications, you can more accurately choose the type of conveyor belt that suits your needs. Whether it is higher strength or thicker cover layer, understanding the meaning of these numbers and letters can help you choose the most suitable product.
4.2 Common Representation Formats and Standards
The representation format of EP conveyor belts may vary depending on the manufacturer and region. But in most cases, the specifications of EP conveyor belts follow a certain standard format. For example, the EU and the United States often mention the specific number of layers, strength grade and cover layer thickness in the conveyor belt standards so that both buyers and sellers can have a unified understanding.
Common standard formats include:
- EP500/3: This representation indicates that the strength grade is 500 N/mm and the belt has two layers of carcass ply.
- EP500/3 6+3:This specification indicates a strength grade of 500 N/mm, with three layers of carcass ply, 6 mm of top top cover and 3 mm of bottom cover.
These representation methods help consumers quickly understand the basic structure and applicable environment of the conveyor belt, and facilitate comparison between multiple products.
4.3 Identification and Labeling Standards
There are also strict specifications for the identification and labeling of conveyor belts to ensure the authenticity of the product and meet the corresponding quality standards. According to international and regional standards, the label of EP conveyor belts usually includes:
- Manufacturer information:including the name and contact information of the manufacturer to help customers trace the source of the product.
- Specification number: details the strength, number of layers, thickness of the cover layer, etc. of the conveyor belt.
- Certificate of conformity: certification marks and certificates that prove that the conveyor belt meets industry standards, such as ISO certification.
- Production date:The production date is usually indicated on the label to help customers understand the production cycle of the product and facilitate subsequent management.
Clear identification not only ensures the quality and legality of the product, but also provides users with better after-sales service guarantees. If you are considering purchasing EP conveyor belts, make sure that the products you purchase meet the relevant identification specifications to avoid purchasing inferior or substandard conveyor belts.
5. Specifications of EP Belts
When choosing an EP conveyor belt, it is essential to understand its detailed specifications. The above article only gives a brief description. Next, I will take you into the world of EP conveyor belt specifications, and describe the corresponding specifications based on some actual situations to facilitate your understanding.
5.1 Materials
The core materials of EP conveyor belts include polyester and nylon. The excellent combination of these two materials gives the conveyor belt good strength, tension resistance and wear resistance. In addition to these two, there are also different materials such as steel cord, which are not described here. Different materials and different weaving methods will affect the overall performance of the conveyor belt. Therefore, when choosing, you should choose the appropriate combination according to the actual use scenario.
5.2 Number of Plies
The number of plies of a conveyor belt can affect its strength and load-bearing capacity to a certain extent. The number of plies of an EP conveyor belt is usually determined by the number of EP plies. Generally speaking, the more plies, the stronger the load capacity of the conveyor belt, but the weight will also increase. Therefore, it is critical to choose the right number of layers, which should be determined according to the specific working load and use conditions.
5.3 Belt Strength
Belt strength refers to the maximum tensile force that the conveyor belt can withstand under normal use conditions, usually expressed in Newtons per millimeter (N/mm). The higher this value, the stronger the conveyor belt’s carrying capacity. When purchasing EP conveyor belts, pay special attention to choosing the right belt strength according to the actual load requirements.
For example, EP300 means that the conveyor belt has a strength of 300N/mm, while EP100 means a strength of 100N/mm. If your application scenario requires a larger load or a higher operating speed, you may need to choose a stronger EP conveyor belt.
5.4 Belt Thickness
The thickness of the conveyor belt directly affects its durability and applicability. Generally, the thickness of an EP conveyor belt is determined by the thickness of its EP layer and cover layer, as well as the interlayer between the EP layers. Generally speaking, the thicker the belt, the stronger its load-bearing capacity and wear resistance, but the same principle as the number of layers, as the thickness increases, the weight will also increase, and the flexibility will be relatively reduced.

5.5 Belt Width
The belt width determines the width of the goods that the conveyor belt can accommodate. When selecting an EP conveyor belt, it is very important to determine the required belt width because it directly affects the conveying efficiency and the adaptability of the device.
Common belt widths are 600mm, 1000mm, 1200mm, etc., but with our latest technology, we can expand the width to 6500mm, allowing our conveyor belts to adapt to wider usage scenarios
5.6 Cover Thickness
The thickness of the cover layer is also an important factor affecting the durability and applicability of the conveyor belt. The top and bottom covers of the EP conveyor belt are usually made of rubber materials, which can effectively protect the reinforcement layer from the external environment and extend the service life of the conveyor belt.
For example, conveyor belts with thicker top covers are usually suitable for environments that require impact resistance and wear resistance, while thinner covers are suitable for those that require high-speed and high-frequency working environments. Selecting the appropriate cover thickness according to the specific operating environment and working conditions will help improve the overall performance and efficiency of the conveyor belt. In addition, the top and bottom covers do not have to be completely equal in thickness. Since the bottom cover does not need to directly transport the goods, in most cases, the bottom cover can be appropriately thinner, which can appropriately save costs.
5.7 Cover Grade
Cover grade refers to the durability and adaptability level of the cover. Different cover grades are suitable for different working environments. Cover grades can be divided into multiple types according to the specific needs of the workplace. Selecting the appropriate cover grade can ensure that the conveyor belt operates stably under harsh conditions and avoid downtime or replacement due to cover damage.
Different physical forms will be available according to different national standards and different types. For example, in the DIN-Y standard mentioned above, DIN stands for German standard, but in addition to DIN national standard, there are also RMA standards, etc., and in addition to Y-type, there are also different types such as W, X, and Z. Their tensile strength and elongation have different parameter standards. If you are not an engineer, it is recommended that you communicate with the engineer before making a decision.
5.8 Temperature Range
The operating temperature range of EP conveyor belts depends on the temperature resistance of its material. Common EP conveyor belts usually work in ambient temperatures between -10°C and +60°C, but if they need to be used at more extreme temperatures, you may need to choose belts with special temperature resistance. For example, in high temperature environments, heat-resistant cover materials and special rubber materials can ensure the long-term stable operation of conveyor belts.
6. EP conveyor belt layers: more is better?
When choosing EP conveyor belts, the choice of the number of layers is critical. Many people may think that the more layers, the stronger the conveyor belt is and the wider the application occasions. But in fact, the choice of the number of layers is not the more the better. It needs to be based on the actual application needs, load capacity requirements, system flexibility, and even the money in your pocket to make a reasonable judgment.
6.1 The impact of the number of layers on strength and load capacity
First, let’s analyze the importance of the number of layers from the perspective of strength and load capacity. The number of layers of a conveyor belt directly affects its strength and load capacity. Simply put, the more layers, the stronger the conveyor belt’s load capacity. For some industries that need to transport heavy materials, such as mining and metallurgy, it is a wise choice to choose an EP conveyor belt with more layers. Generally speaking, EP conveyor belts with 4 layers or more are suitable for heavy load occasions, can withstand greater pressure, and adapt to long-term high-load working conditions.
However, there are certain disadvantages to too many layers. In the case of low load requirements, too many layers not only waste materials, but also increase the weight and cost of the conveyor belt. Overweight conveyor belts may increase friction and energy consumption of equipment, thereby reducing the efficiency of the system. Therefore, when choosing the number of layers, make sure not to over-configure and avoid the situation of “too much is as bad as too little”.
6.2 The trade-off between the number of layers and flexibility
Next, we will talk about the impact of the number of layers on the flexibility of the conveyor belt. In some occasions that require flexibility and a smaller bending radius, it is more appropriate to choose an EP conveyor belt with fewer layers. Fewer layers make the conveyor belt more flexible and able to adapt to complex conveying paths, especially in environments that require more turns or bends. If you are working in relatively small spaces such as automated warehousing and production lines, choosing a 2-layer or 3-layer EP conveyor belt can effectively improve conveying efficiency and reduce transportation resistance and jamming problems caused by too hard belts.
On the other hand, if there are too many layers, the belt becomes thicker and more rigid, which may cause it to be uncomfortable when bending, and even affect the normal operation of the conveying system. Therefore, flexibility is another important consideration when choosing the number of layers. Choosing the appropriate number of layers according to the path of the conveyor belt and the required turning radius can make the system run more smoothly.
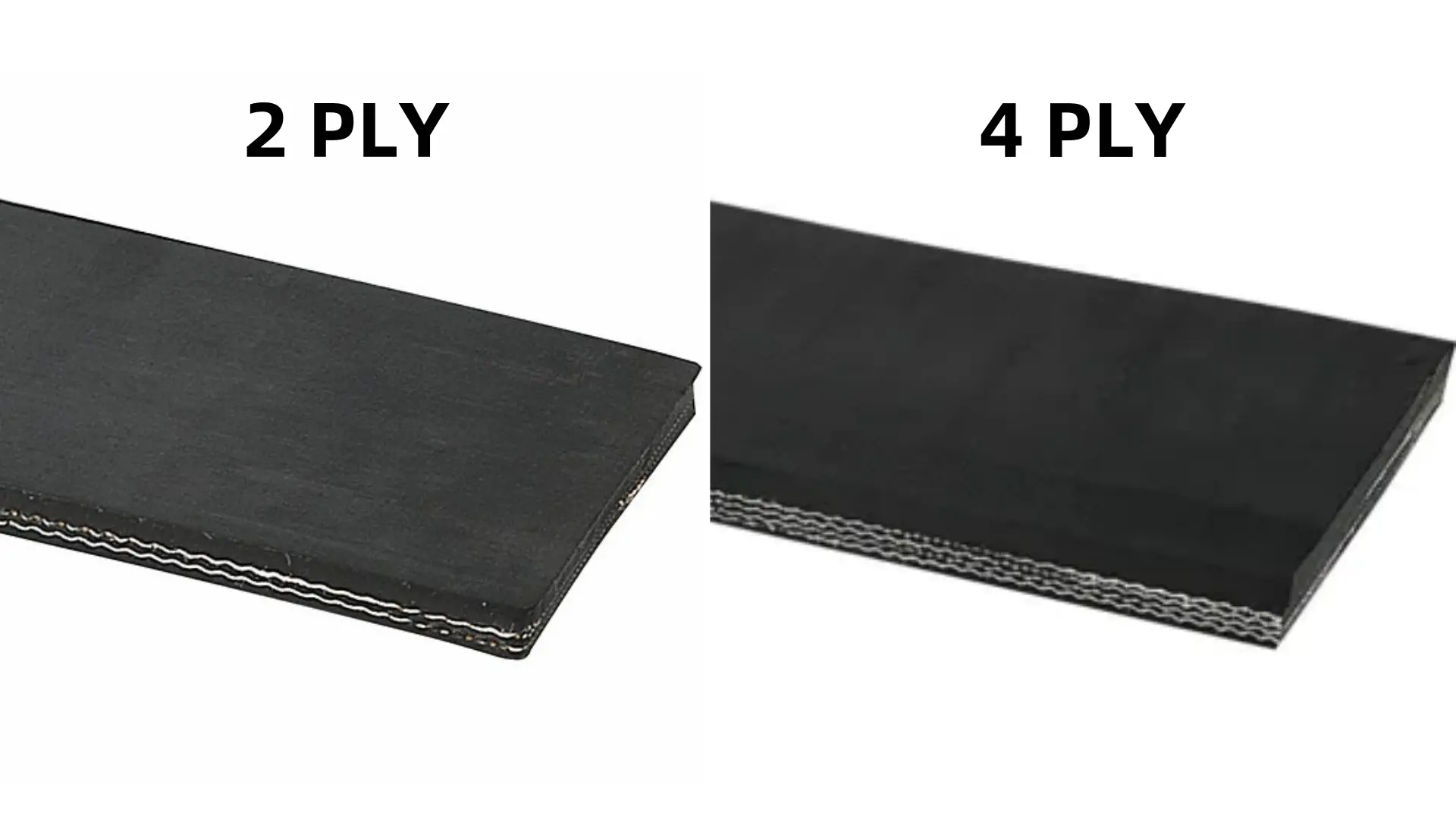
6.3 The impact of the number of layers on cost and weight
In addition to strength and flexibility, the choice of the number of layers also has a great impact on cost and weight. More layers means higher material costs, because more layers require more raw materials. At the same time, too many layers will also increase the weight of the conveyor belt, which will also have a certain impact on the load-bearing capacity and energy consumption of the equipment. Especially in situations where energy efficiency is required, belts with too many layers may make the system operate more inefficiently.
Conversely, belts with fewer layers are relatively cheap and lighter, suitable for low-load, high-efficiency working environments. Therefore, when choosing, it is necessary to fully balance cost and performance. Some economical application scenarios can meet the load requirements without adding unnecessary expenses by choosing EP conveyor belts with a moderate number of layers.
6.4 The best number of layers for different application scenarios
The requirements of each application scenario are different, and the choice of the number of layers often depends on the specific operating environment and work requirements. Here are some common application scenarios and their recommended number of layers:
- Heavy load transportation:If you are working in a heavy load environment such as a mine, metallurgical plant or steel industry, EP conveyor belts with more than 4 layers will provide more strength and durability. Such environments have high load requirements for conveyor belts. Multi-layer belts can effectively support the long-term operation of heavy materials and reduce the cost and trouble of frequent belt replacement.
- General material transportation:For general material transportation (such as sand, gravel, building materials, etc.), it is usually sufficient to choose 2-layer or 3-layer EP conveyor belts. This type of belt can meet the load requirements without making the cost too high, and is suitable for occasions that do not require ultra-high load capacity.
- Complex environment and high temperature conditions:In high temperature or chemically corrosive environments, in addition to considering the number of layers, the cover material of the EP conveyor belt is also a key factor. For such environments, choosing a belt with a moderate number of layers and combining a cover material that is resistant to high temperature and chemical corrosion can better cope with extreme working conditions.
- Systems that require bending or small turns:If the conveyor belt needs to operate in an environment with many bends (such as workshops, warehouses, etc.), EP conveyor belts with fewer layers will be more flexible. This ensures that the conveyor belt is not prone to jamming or breaking when turning, while reducing friction.

It can be seen that choosing the number of layers of EP conveyor belts is not just about pursuing more, but making the most appropriate choice based on actual needs. Although too many layers provide stronger load-bearing capacity, they may also increase costs and weight, so comprehensive considerations are needed. Next, we will explore how to choose the appropriate EP conveyor belt specifications according to different operating conditions and usage requirements, including factors such as belt width, thickness, and strength.
7. How to choose the right EP conveyor belt
Choosing the right EP conveyor belt is not only about understanding the basic elements such as the number of layers and strength of the belt itself, but also requires a comprehensive understanding of the needs of the entire transportation system. From load capacity to use environment, from installation requirements to cost budget, details determine success or failure. Therefore, how to accurately choose a suitable EP conveyor belt is the key to ensuring the stable operation of the system.
7.1 Load capacity and belt strength
When choosing an EP conveyor belt, you need to give priority to the weight of the conveyed material, the running time of the conveyor belt, and whether there is an extreme working environment. The strength and load capacity of the EP conveyor belt are closely related to the number of layers, upper and lower covering layers and their thickness of the EP belts.
For ordinary material transportation (such as small and medium-sized materials), we usually recommend customers 2-3 layers of EP300 conveyor belts, which are more stable. Of course, some customers will also choose the cheaper EP100/2; for heavy or long-term applications (such as ore, steel, etc.), you need to choose more layers of EP conveyor belts to ensure strength and durability, which may require EP630/4 or EP630/5.

7.2 Selection of belt width and thickness
How to choose the width and thickness of the conveyor belt? This is closely related to the size of the conveyed material, the transportation distance, and the speed of the conveyor belt. Wider conveyor belts are suitable for conveying large materials or high-capacity materials, which can reduce the accumulation or overflow of materials during transportation, but this has certain requirements for the number of EP layers.
When choosing the width and thickness, it is necessary to match the design of the equipment. When the conveyor belt is too wide, the edge of the conveyor belt may rub against the roller column. When the conveyor belt is too thick, the weight of the conveyor belt itself will increase. In addition, the pressure-bearing weight of the product during operation will increase the excessive friction between the lower surface of the conveyor belt and the roller, resulting in a reduction in the life of the conveyor belt, and at the same time increase the operating pressure of the driving roller.
7.3 Evaluation of operating conditions
In addition to basic physical parameters, operating conditions are also a key factor to consider when selecting EP conveyor belts. The content involved here includes:
- Temperature:Are you using the conveyor belt in a high or low temperature environment? Different ambient temperatures have different effects on the material and cover of the belt. When selecting, make sure that the temperature adaptation range of the belt meets the requirements of the operating environment. When the temperature is too low, the rubber will become hard and brittle, which will reduce the stability of the rubber conveyor belt and affect operation and safety. When the temperature is too high, it will accelerate the aging of the rubber on the surface of the conveyor belt.
- Humidity and chemical exposure:If the conveyor belt is exposed to a humid environment or needs to transport corrosive materials, then the cover material with good water resistance and chemical resistance is essential. This determines the service life and maintenance cost of the conveyor belt.

7.4 Flexibility
For some more complex conveying systems, especially in environments that require high-density operations, flexibility becomes the key to selection. In this case, it is more suitable to choose a lighter EP conveyor belt with a moderate number of layers. Lighter belts can quickly adapt to different operating requirements, while heavier or too many layers of belts may not meet the flexible requirements of the system due to excessive rigidity.
7.5 Durability
Durability directly determines the service life of a conveyor belt, and also directly determines the maintenance cost and replacement frequency. If the conveyor belt needs to be replaced frequently, this will undoubtedly increase additional operating costs and affect overall production efficiency, and will increase many intangible costs, such as time costs. Therefore, when choosing, consider how different belts perform under long-term high loads, high temperatures, or harsh environments. Choosing a durable EP conveyor belt will save your business a lot of time and money, and part of this is related to the supplier you choose.
7.6 Cost and Budget Considerations
Cost is always one of the important factors in business decision-making. When choosing an EP conveyor belt, make sure to make a reasonable decision based on cost and budget. Although high-performance, durable belts are more expensive, they generally provide longer service life and lower maintenance costs, and save you a lot of time costs. Choosing a cheaper belt may save money in the short term, but it may lead to frequent replacement and repair, which increases the hidden cost of long-term operation.
Try to think about it, if you buy a product for 8,000USD twice a year and replace it twice, and spend 10,000USD to buy it once a year and replace it once, I think you will choose the 10,000USD one anyway. Therefore, the right approach is to consider the initial investment and long-term maintenance costs and choose a solution with the best cost-effectiveness.

7.7 Detailed explanation of selection steps
Selecting the right EP conveyor belt is not a one-shot process. It usually requires the following steps:
- Evaluate the working environment:Understand the basic requirements of the use scenario, including temperature, humidity, chemical exposure, etc.
- Determine the load requirements:Determine the required belt strength based on the weight of the material being conveyed and the transportation time.
- Select the appropriate specifications:Select the appropriate specifications based on the width, thickness and number of layers of the belt.
- Consider the ease of installation and maintenance:According to the design of the equipment and the frequency of use of the conveyor belt, choose a belt that is easy to install and maintain.
- Budget and cost analysis: Finally, weigh the relationship between performance and price based on the budget and select the most suitable EP conveyor belt.
8. Maintenance and maintenance of EP conveyor belt
No matter how many layers of EP conveyor belts are chosen, good maintenance and upkeep can significantly extend its service life and improve the efficiency of the conveyor system. During long-term use, the conveyor belt may encounter problems such as wear and aging, and correct maintenance methods are particularly important at this time. How to maintain the best condition of the conveyor belt and avoid unnecessary losses caused by improper operation is a core skill that every user needs to master.
8.1 Regular inspection of conveyor belts
To ensure that the EP conveyor belt is always in optimal working condition, regular inspection is a step that cannot be ignored. Regular inspections can detect potential problems early and prevent minor problems from turning into major failures. Generally speaking, you can check according to the following aspects:
- Surface inspection:Observe the surface of the conveyor belt for cracks, wear, cuts or other signs of damage. If there is obvious damage to the surface, it may affect the material conveying efficiency or even cause the belt to be completely damaged.
- Tension check:Check whether the tension of the conveyor belt is appropriate. Too loose or too tight tension will affect the service life of the conveyor belt. Depending on the model of the conveyor belt, adjust the tension appropriately to ensure that it does not wear excessively during operation.
- Alignment check:Ensure that the conveyor belt always maintains good alignment during operation. If the conveyor belt deviates from the center line, it will cause local wear and may even cause the conveyor belt to jump out. Regular inspection and alignment adjustments are key to maintaining stable operation of your conveyor system.
8.2 Cleaning and dust removal
During the use of conveyor belts, especially in dusty environments, it is easy to accumulate material residue and dust. These debris will increase the friction of the conveyor belt, leading to increased belt wear. Therefore, regular cleaning is very necessary.
- Surface cleaning:Use appropriate cleaning tools and detergents to gently wipe the surface of the conveyor belt. Avoid using rough tools to avoid scratching the surface of the belt.
- Dust removal:If dusty materials are transported, it is recommended to install a dust removal device on the conveyor belt, or use special cleaning equipment for regular cleaning to reduce dust damage to the conveyor belt.

8.3 Prevent excessive wear
Wear is the biggest enemy of conveyor belt performance, especially under high-load or high-speed operating conditions, where wear will accelerate. To reduce wear and tear, you can do the following:
- Avoid material accumulation:Clean the material residue on the conveyor belt regularly to avoid long-term material accumulation and increase the burden on the conveyor belt.
- Optimize the running speed:Too fast running speed will increase the wear of the conveyor belt, so the speed of the conveyor belt should be reasonably adjusted according to the actual situation to ensure that it operates in the best condition.
- Reasonable selection of conveyor belt types:For rougher or sharp materials, you can choose conveyor belts with higher wear resistance on the surface, such as wear-resistant EP conveyor belts, to reduce wear.
8.4 Adjust the running angle of the conveyor belt
The angle of some conveyor systems changes greatly, and long-term uphill or downhill operation may cause uneven load on the conveyor belt, thereby causing damage to the belt. To avoid this, you can:
- Adjust the running angle:Ensure that the running angle of the conveyor belt does not exceed the maximum angle specified in the design to avoid excessive inclination angles causing additional pressure on the belt.
- Add auxiliary devices:In inclined conveyor systems, auxiliary devices (such as supports or rollers) can be installed to help relieve the pressure on the conveyor belt and reduce wear caused by angle changes.
8.5 Check joints and connections
The joints and connections of conveyor belts are areas prone to failure. Especially when conveyor belts need to be replaced quickly, the quality of joints and connections directly affects the operating efficiency and safety of the conveyor system. Common inspection items include:
- Joint inspection:Regularly check whether the joint part is firmly fixed to avoid loosening or falling off of the joint.
- Connection status:Make sure the connection part is not loose, corroded or damaged. If there is any problem with the connection part, repair or replace it in time.

8.6 Prevent high temperature and ultraviolet exposure
If the conveyor belt is exposed to high temperature or ultraviolet light for a long time, it will easily lead to material aging, cracking and other problems. Therefore, special attention should be paid to avoiding the following problems when installing conveyor belts:
- Avoid excessively high operating temperatures:Try to avoid operating the conveyor belt under conditions that exceed its high temperature resistance range. If the system’s working environment temperature is high, you can choose a high-temperature-resistant EP conveyor belt, or consider installing a temperature control device for the conveyor belt.
- Avoid UV exposure:Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight, especially conveyor belts operating outdoors, can easily lead to aging. Therefore, the conveyor belt can be provided with sun protection measures or a UV-resistant belt material can be selected.
8.7 Ensure proper lubrication
For some special types of conveyor belt systems, proper lubrication can reduce friction, reduce wear, and improve the efficiency of the system. The use of lubricating oil or grease should be selected according to the material of the conveyor belt and the working environment to avoid damage to the surface of the conveyor belt due to improper lubrication methods.
9. How to Request for More Accurate Quote? Required Parameters
Getting an accurate quote for EP conveyor belts is not a complicated matter, but you need to provide some key information. Only by ensuring the accuracy of these parameters can you get the quote that best meets your needs. The following are several important factors affecting the quote.
9.1 Key Parameters Affecting Quotes
9.1.1Material Type and Quality
The material of the conveyor belt will directly affect the price. High-quality EP materials, such as high-strength polyester and nylon combinations, are naturally more expensive, but their durability and performance are also better.
9.1.2Belt Specifications
It is necessary to clarify the specifications of the conveyor belt, such as width, thickness, length, and number of plies. The prices of conveyor belts of different specifications vary greatly.
9.1.3Number of Plies and Structure
The more plies an EP conveyor belt has, the stronger its strength and load-bearing capacity will be, and the corresponding quotation will be higher.
9.1.4Special requirements
If you have special performance requirements (such as high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance or anti-static, etc.), the quotation will naturally be different.
9.1.5Delivery Time and Quantity
Bulk purchases and pre-arranged delivery times usually have more favorable prices. In the case of urgent delivery, the price may be higher.
9.1.6Mode of transportation
Sea, air, or land, different modes of transportation, the price is naturally different, this is usually based on the freight forwarder’s quotation.
9.1.7Trade terms and payment methods
Trade terms in international trade need to be understood clearly, EXW, FOB, CIF, etc. What do these trade terms mean, when do you need to receive the goods, and what should be paid attention to under what conditions for different terms?
For example, if you need your supplier to quote FOB prices, you need to confirm with your supplier the nearest port to your supplier’s factory, and then find your designated freight forwarder, but if you use CIF terms, you only need to tell your supplier where the nearest port is, and the rest is up to your supplier to find a suitable freight forwarder to be responsible for shipment.

9.2 How to Prepare a Quote Request
9.2.1Detailed Description of Requirements
In the quotation request, you need to provide a clear description of the requirements, preferably including the specific application scenarios and operating environment requirements of the conveyor belt.
9.2.2Providing Accurate Specifications and Parameters
Provide the detailed specifications of the conveyor belt mentioned above, including width, thickness, number of layers, length, etc. The more detailed the better. This will allow suppliers to provide accurate quotations based on these requirements.
9.2.3Selecting the Right Suppliers
When selecting a supplier, in addition to price, factors such as its reputation, delivery capabilities, and after-sales service should also be considered.
9.3 Tips to Improve Quote Accuracy
9.3.1Clear Communication
Communication with suppliers should be clear and unambiguous to avoid quotation deviations due to information asymmetry.
9.3.2Advance Planning
Plan the requirements and procurement plans in advance, especially in terms of quantity and delivery time, to ensure that you can reach a consensus with the supplier.
9.3.3Comparing Multiple Suppliers
Comparing quotations from multiple suppliers is not just about price, but also about quality, service and other factors.
9.3.4Leveraging Industry Standards
Using industry standards to guide your selection and quotation requests can ensure that your requirements are in line with the norm and that the quotations provided by suppliers are more accurate.
9.3.5Decisiveness in purchasing
This is a very difficult question to explain. Many of our customers have a problem. After getting the quotation, they need to communicate with the team and think about it. Then a week or two passes. Rubber is a futures product. Maybe during the process of your consideration, the price of its raw materials has increased. At this time, your supplier may have no choice but to increase the price. At this time, you may need to spend more money to purchase again.
10. Maintaining EP Belts: Longevity Tips
EP conveyor belts are widely used in various industries due to their superior performance, but proper maintenance is essential to ensure their long-term effective operation. Proper maintenance can not only extend the service life of the conveyor belt, but also improve the operating efficiency of the equipment and reduce production downtime. Here are some practical tips for maintaining EP conveyor belts to help you keep your conveyor belts in optimal condition.
10.1 Maintenance Tips for EP Conveyor Belts
10.1.1Regular Cleaning
Conveyor belt cleaning is essential for its long-term stable operation. Regularly removing material residues, dust and impurities from the conveyor belt can prevent material accumulation, reduce friction and avoid damage to the conveyor belt surface. Avoid using strong acid or strong alkaline detergents when cleaning to avoid damaging the belt surface. It is recommended to use a mild detergent and a soft brush for cleaning.
10.1.2Check the alignment
Alignment problems of conveyor belts are often the root cause of wear. Check the alignment of the conveyor belt regularly to ensure that the conveyor belt runs along the correct path. A deflected conveyor belt not only increases belt wear, but also puts additional stress on the drive system. Alignment can be done by adjusting the pulleys or replacing the offset sensor.
10.1.3Maintain Proper Tension
Excessive or insufficient belt tension will affect the service life of the conveyor belt. Excessive tension will cause tearing and premature wear of the conveyor belt, while insufficient tension may cause slippage and inefficient transmission. It is recommended to adjust the tension according to the specifications and load conditions of the conveyor belt, and regularly check whether the tension remains in the appropriate range.
10.1.4Regularly check and replace rollers
Rollers are key components that support the conveyor belt. Any damaged or unbalanced rollers will affect the smooth operation of the conveyor belt. Regularly checking the working condition of the rollers and replacing worn or damaged rollers in time can ensure that the conveyor belt always runs in the best condition.
If you need advice and tips on maintenance, please refer to this article for details:
5 Conveyor Belt Maintenance Tips to Minimize Downtime and Risks
10.2 Common Issues Faced with EP Belts and How to Address Them
10.2.1Wear Problems
EP conveyor belts are prone to wear after long-term use, especially when the material is rough or sharp. The solution is to regularly check the surface of the conveyor belt and replace or repair it in time when signs of wear are found. In addition, the use of anti-wear coverings can also effectively extend the service life of the belt.
10.2.2Cracks and tears
If the EP conveyor belt is under high load for a long time, cracks or tears may occur. At this time, it is recommended to stop the equipment operation in time and repair or replace the damaged part. You can also use a special conveyor belt repair glue for local repair to extend the service life.
10.2.3Deviation problem
Conveyor belt deviation is one of the common faults, usually caused by uneven tension or roller problems. The solution is to regularly check the wear of the pulleys and rollers and ensure their alignment. If the conveyor belt deviates, adjust the tension and repair related parts in time.
For solutions to this problem, please refer to the following article:
10.3 Importance of Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspection and maintenance are key factors in extending the service life of EP conveyor belts. Through regular inspections, potential problems can be discovered in advance to avoid equipment failures and unexpected downtime. For example, checking the wear of the belt, the operation of the rollers, and the working condition of the drive system can solve problems in time and ensure smooth operation of the equipment.
In addition to daily inspections, it is also necessary to conduct a comprehensive overhaul every year. A comprehensive inspection includes replacing severely worn rollers, adjusting the tension of the conveyor belt, cleaning the accumulated materials, and checking the drive system, all of which can effectively extend the service life of the conveyor belt.

10.4 Best Practices to Extend the Lifespan of EP Conveyor Belts
Choose the appropriate EP conveyor belt specifications, such as strength, width, thickness, etc., according to the specific application requirements. Excessive loads and inappropriate specifications will accelerate the wear of the conveyor belt and shorten its service life.
10.4.1Regular lubrication
Regular lubrication of the moving parts of the conveyor belt, such as pulleys and drive devices, can reduce friction and wear, thereby extending the service life of the parts.
10.4.2Use guards
Using guards in the working area of the conveyor belt can effectively avoid contact with sharp objects, hot substances or chemicals, thereby reducing damage to the conveyor belt.
10.4.3Control the working environment
Control the temperature, humidity and other factors in the working environment to avoid the conveyor belt working under extreme conditions. Too high or too low temperature may cause the material to become brittle or soften, reducing the service life of the conveyor belt.
EP conveyor belts are undoubtedly one of the most popular choices on the market. They have won wide favor with their unique structure, sturdy performance and flexible application. If you are looking for a conveyor belt that can provide strong support and meet a variety of industrial needs, EP belts are definitely an option worth considering. By understanding the characteristics of EP belts and how they work in different applications, you can better understand why they are so popular.
Of course, whether the EP conveyor belt is suitable should also be determined in combination with specific operating requirements and usage environment. If you have more questions about EP conveyor belts or need a customized solution, please feel free to contact us! We will provide professional advice and support based on your needs to ensure that you make the most appropriate choice. Contact us now and let us find the conveyor belt solution that best suits you!


















